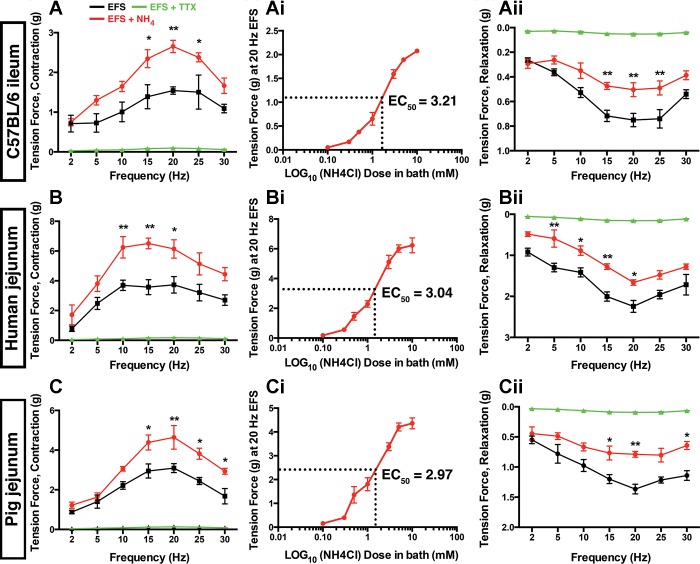
Fig. 1.
NH4Cl alters neuromuscular transmission in the mouse, human and pig intestine. Electrical field stimulation (EFS; 20 V, 0.3 ms, 2-30 Hz) frequency-response curves for neurogenic contractions and relaxations in segments of ileum and jejunum from mice (A), humans (B), and pigs (C) in the presence (red) or absence (black) of NH4Cl (5 mM). Contractions (A, B, and C) and relaxations (Aii, Bii, and Cii) driven by EFS are abolished in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX; 0.3 μM; green). Ai, Bi, and Ci: dose-response curves showing the effect of ascending concentrations of NH4Cl on contractions driven by 20-Hz EFS in mice, humans and pigs. EC50 values for NH4Cl are given for each at right. Data are means ± SE and were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferonni’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control (n = 5 in each group).