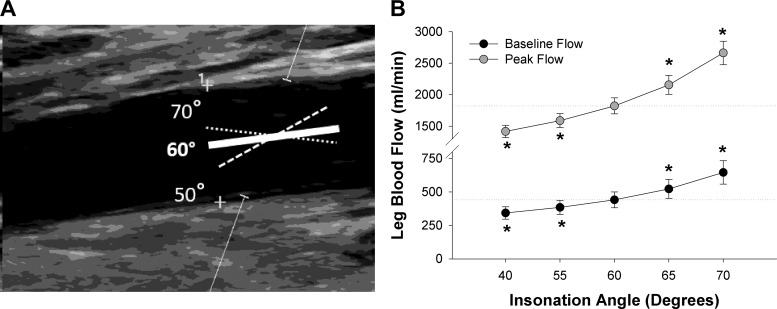
Fig. 5.
Effect of insonation angle on measurements of leg blood flow during passive leg movement (PLM). A: representative image of Doppler ultrasound with the angle correction cursor (solid line) acceptably aligned with the artery at an insonation angle of 60° from the Doppler beam or out of alignment with the artery walls at either 50 or 70° from the Doppler beam. The cross hairs on artery wall represent location of the media layer where diameter measurements were made. B: effect of error in insonation angle (i.e., misalignment of angle correction cursor with the artery wall) on resting blood flow and peak blood flow during PLM (n = 5). Note that the acceptable error condition was taken as an accurately determined insonation angle of 60° with the angle correction cursor parallel to the artery. Dashed lines represent mean value at the acceptable error associated with this 60° insonation angle for each condition. *Significantly different from the acceptable error associated with an insonation angle of 60°.