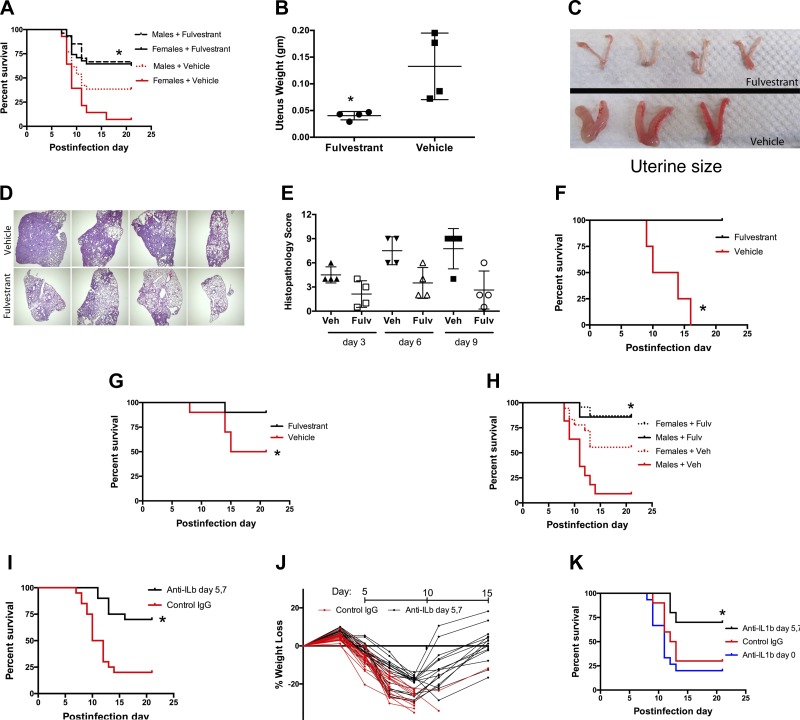
Fig. 4.
Estrogen receptor blockade is protective during influenza infection. A: the estrogen receptor antagonist fulvestrant (200 μg ip every other day, starting day 21 of age) before infection of 28-day-old mice improves survival in both pubertal males and females compared with vehicle-treated mice (*P = 0.049 for male mice, P < 0.001 for female mice, n > 26/group, summary of 3 trials). B and C: fulvestrant prevents the estrogen-dependent pubertal increase in uterine weight (B) and size (C) (*P = 0.02, n = 4, harvest at age day 35, Mann-Whitney test). D and E: lung histopathology shows less consolidation and injury in fulvestrant-treated female mice, illustrated by low-power views of samples taken 9 days after infection (D) and lung injury scores (E) for samples taken 3, 6, and 9 days after infection (*P = 0.0005, Kruskal-Wallis test). F: delayed treatment with fulvestrant, started 3 days after infection of 28-day-old pubertal female mice, improves survival compared with vehicle-treated mice (*P = 0.007, n = 4/group). G: fulvestrant started 7 days before infection in older 42-day-old female mice improves survival compared with vehicle-treated mice (*P = 0.06, n = 10/group, single trial). H: estrogen receptor blockade with fulvestrant started 3 days after infection in 42-day-old female and male adult mice improves survival compared with vehicle-treated mice (*P = 0.019 for female mice, P < 0.0001 for male mice, n > 19/ group, summary of 3 trials). I and J: treatment of P28 female mice on days 5 and 7 after influenza virus infection with 100 μg ip of anti-IL-1β neutralizing antibody improves survival (*P = 0.0009, n = 20/group, summary of 3 trials; I) and allows recovery from the initial weight loss (J). The control group received hamster IgG isotype antibody. K: after influenza virus infection, early treatment (day 0) with anti-IL-1β antibody provides no benefit, in contrast to improved survival seen with delayed treatment 5–7 days after infection (*P < 0.01 vs. control or day 0 treatment; n = 10 for control IgG, delayed treatment groups; n = 15 for early treatment; single trial).