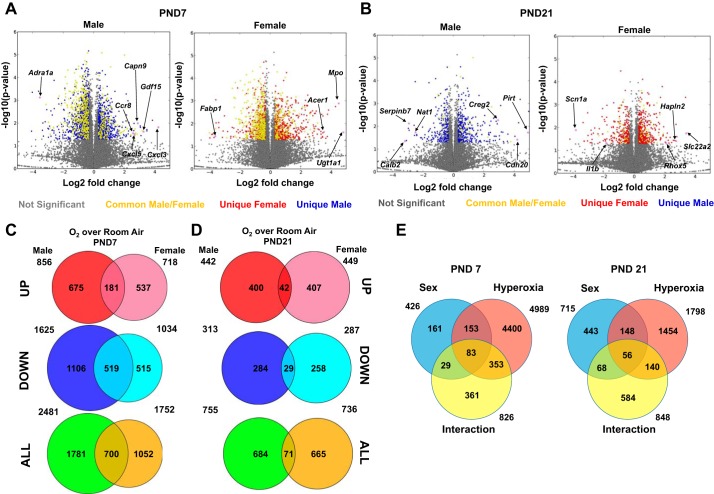
Fig. 2.
Distinct pulmonary transcriptomic responses were noted in male and female neonatal mice after exposure to hyperoxia. A and B: volcano plots of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs; upregulated and downregulated) in male and female neonatal mice in response to hyperoxia exposure compared with room air controls on PND7 (A) and PND21 (B). The genes shaded in yellow are common DEGs between male and female neonatal mice, whereas the genes represented in blue are DEGs exclusive to male neonatal mice, and those in red are exclusive to female neonatal mice. Select differentially regulated genes are highlighted. C and D: Venn diagrams highlighting the differential gene expression on PND7 (C) and PND21 (D) in male and female neonatal mice exposed to hyperoxia. E: 2-way ANOVA of the pulmonary transcriptome showing effect of hyperoxia, sex, and any interaction between the 2 variables.