Fig. 4.
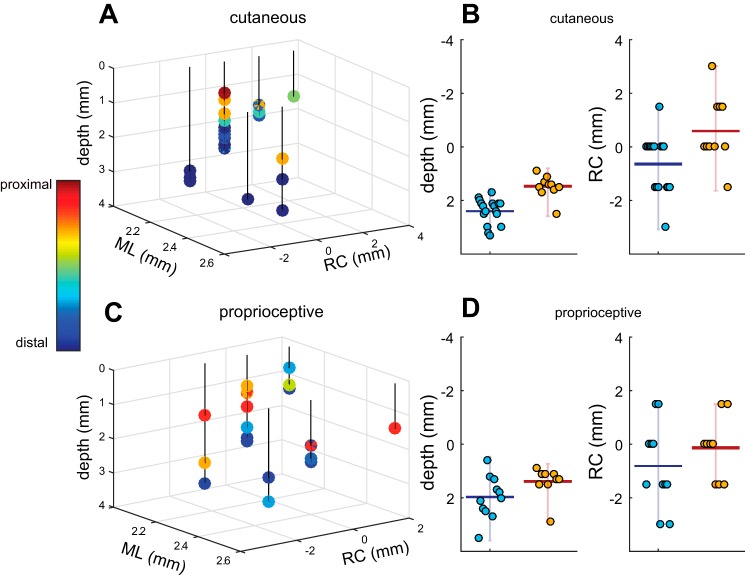
Somatotopic organization of CN. A: 3D diagram of penetrations with cutaneous RFs plotted with respect to obex and the surface. Color bar indicates the RF location. ML, medio-lateral; RC, rostro-caudal. B: summary of cutaneous results. Left: distal units tend to be deeper than proximal units. Horizontal bar represents mean values, and vertical bars span the range of values. Right: distal units tend be more cranial (negative along the RC dimension) than proximal units. The forearm served as the boundary between distal and proximal units in the bar plots. C: 3D diagram of penetrations with proprioceptive responses with respect to obex and the surface. Color bar indicates RF location. D: summary of proprioceptive results. Left: distal units tend to be deeper than proximal units. Right: distal units tend to be anterior to their proximal counterparts. Overall, both proprioceptive and cutaneous modalities exhibited similar somatotopic trends: proximal units were located more superficially and more posterior to the obex than distal units.