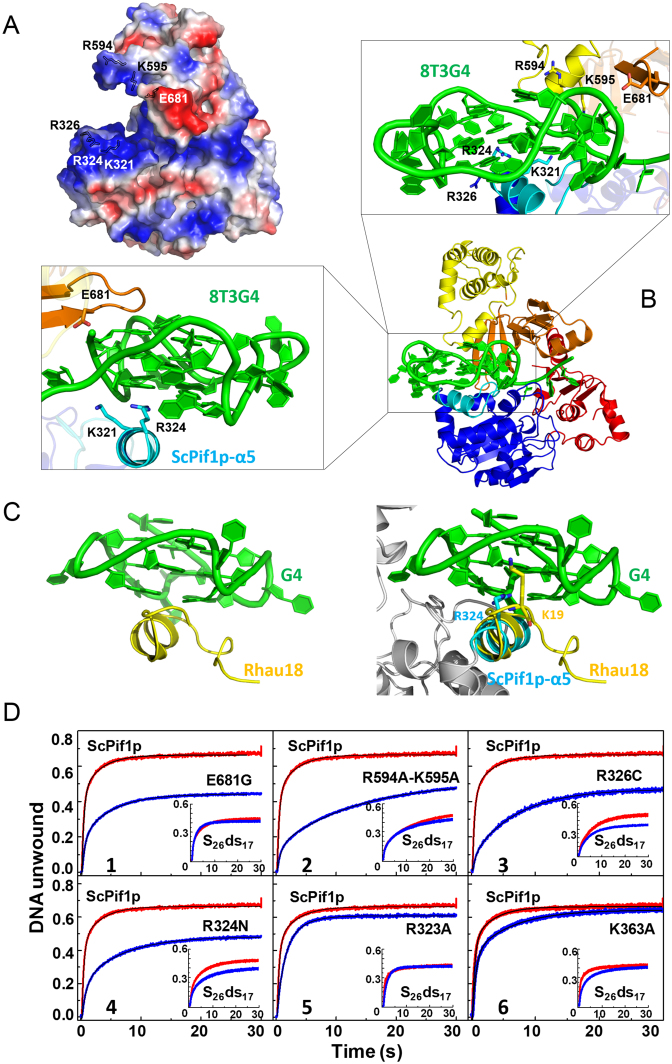
Figure 5.
(A) Molecular electrostatic potential map of ScPif1p with the highly positively charged residues indicated in blue. (B) Molecular modeling model of ScPif1p in complex with G4 DNA. The enlarged boxes (left and up) represent the close-up views of the interactions between the positively charged residues and G4 DNA. (C) Structure of Rhau18-G4 DNA complex determined by NMR (left, PDB entry: 2N21) and superposition of the α-helix RSM in Rhau18 and α5 in ScPif1p (right). (D) DNA unwinding activities of ScPif1p and its variants as determined by stopped-flow fluorescence assay. 4 nM partial duplex DNA (S26ds17) (inset) or G4-containing partial duplex DNA (S26G4ds17) and 100 nM protein were used under experimental conditions as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. The parameters derived from these curves are summarized in Table 2.