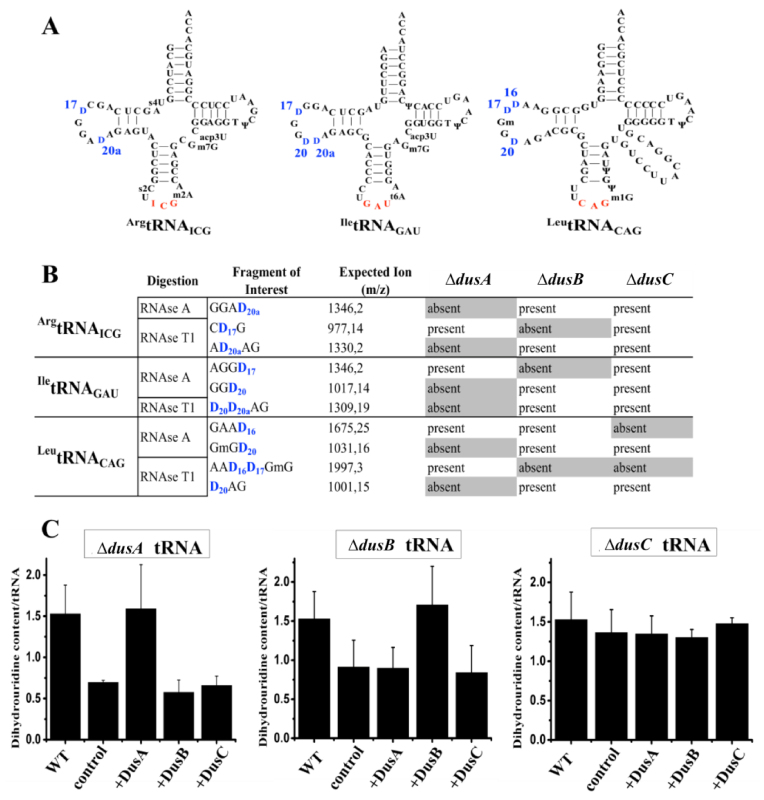
Figure 1.
Identification of Escherichia coli Dus specificity from single knockout strains. (A) Secondary cloverleaf structure and sequence of E. coliArgtRNAICG, IletRNAGAU and LeutRNACAG used in this study. The anticodon is shown in red while the positions of D are labeled in blue. (B) Table showing the D-containing fragment and their sizes (m/z) after RNAse A or T1 digestion of ArgtRNAICG, IletRNAGAU or LeutRNACAG extracted from a wild-type E. coli strain. Presence or absence of these fragments is indicated for each tRNAs originated from ΔdusA, ΔdusB or ΔdusC E. coli strains. (C) In vitro quantification assay of D in E. coli tRNA. For each panel, WT corresponds to the amount of D per tRNA in wild-type bulk E. coli tRNAs. Left, middle and right panels show the amount of D per tRNA in ΔdusA, ΔdusB and ΔdusC bulk E. coli tRNAs, respectively, in the absence of added enzyme (control), or after incubation with the indicated enzymes. Error bars represent the standard error to the mean of three independent experiments.