Figure 1.
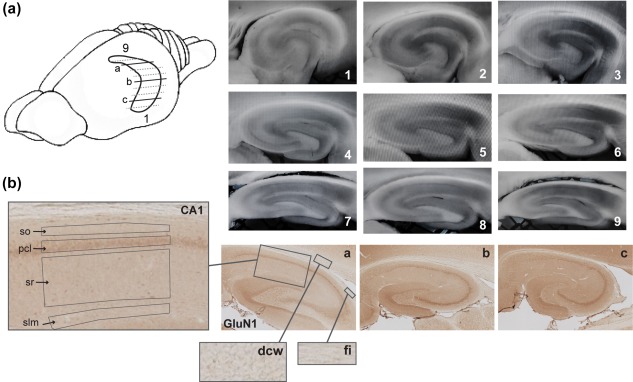
Illustration of hippocampal sectioning and resulting sections throughout its longitudinal axis. (a) A simplified schema of the rat brain showing the horizontally sectioned hippocampus. The amount of lines underrepresents the total amount of slices, which can be obtained from the hippocampus, but highlights the span of sections that could be used for electrophysiological and biochemical processing. Representative immunohistochemically‐stained transverse sections depict dorsal (a), intermediate (b), and ventral (c) hippocampal subdivisions that were used for receptor protein processing (GluN1 subunit of the NMDAR in this case). Sections 1–9 show typical slices used for electrophysiological analysis: Sections 1–3 ventral hippocampal sections; from 4 to 6 represent intermediate, and 7–9 represent dorsal hippocampal slices. (b) A close‐up view of the laminar structure of the hippocampal CA1 region and of receptor‐devoid regions (dcw, deep cerebral white matter tracts; fi, fimbria) used for background (unspecific staining) subtraction. so, Stratum oriens; pcl, pyramidal cell layer; sr, Stratum radiatum; and slm, Stratum lacunosum‐moleculare [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
