Figure 3.
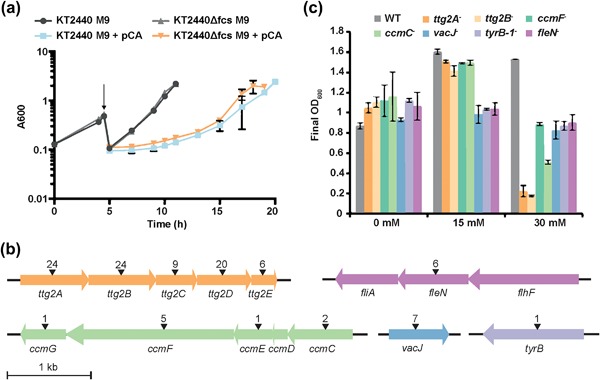
(a) Growth of the Tn5 libraries in P. putida KT2440 and P. putida KT2440 Δfcs in M9 and M9 supplemented with 50 mM of p‐coumaric acid (pCA) is shown. The arrow indicates when p‐coumaric acid was added to the cultures. The growth experiments ended when cells were harvested for DNA sequencing. (b) Some of the most important genes identified to be involved in the tolerance of P. putida KT2440 toward p‐coumaric acid in their genetic landscape. The number of different insertions found in the Tn‐seq assay is shown on top of each gene with arrows. (c) Final OD600 of strains of P. putida KT2440 (WT), ttg2A‐, ttg2B‐, ccmF‐, ccmC‐, vacJ‐, tyrB‐, and fleN‐ at three different concentrations of p‐coumaric acid: 0, 15, and 30 mM. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three independent biological replicates
