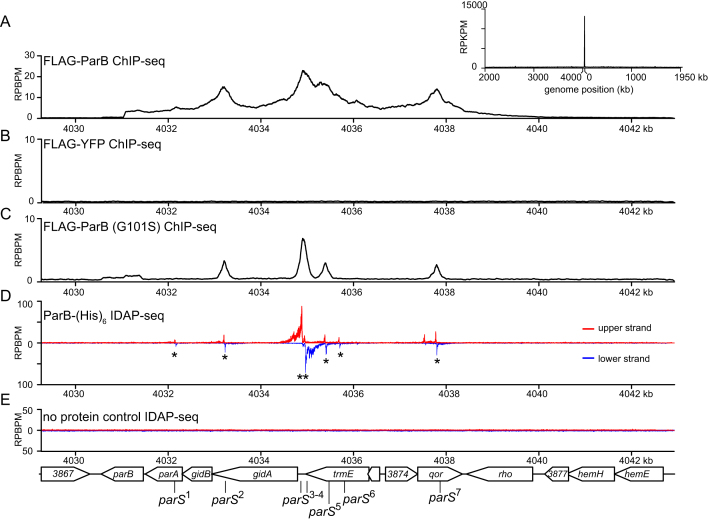
Figure 1.
ParB occupies 10 kb DNA region near the origin of replication. (A) The distribution of FLAG-tagged ParB on Caulobacter chromosome between +4030 kb and +4042 kb. ChIP-seq signals were reported as the number of reads at every nucleotide along the genome (RPBPM value). The whole-genome ChIP-seq profile of ParB is shown in the inset. For the whole genome profile, the ChIP-seq signals were reported as the number of reads at every kb along the genome (RPKPM value). (B) ChIP-seq profile of FLAG-tagged YFP. (C) ChIP-seq profile of FLAG-tagged ParB (G101S) mutant. (D) IDAP-seq profile of ParB-(His)6 with sonication-fragmented genomic DNA from Caulobacter. IDAP-seq reads were sorted to either the upper strand (red) or to the lower strand (blue) of the reference genome to enable identification of parS sites (see also Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S3). Putative parS sites (1–7) are noted with asterisks (see also Figure 2). (E) IDAP-seq profile of a negative control in which ParB-(His)6 was omitted.