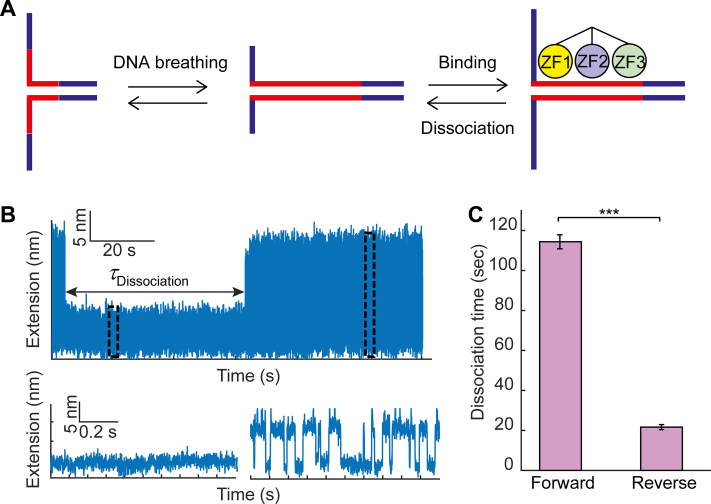
Figure 6.
Force disruption of ZF3 increases Egr-1 dissociation. (A) A single-molecule containing a consensus motif in the C1 context is unzipped until the fork reached the binding site. (B) The construct is held under tension, letting the DNA fluctuate between locally ‘open’ and ‘closed’ states. Binding of Egr-1 to the DNA stabilizes the closed conformation, leading to a sudden repression of the fluctuations, which lasts until Egr-1 dissociation. The time difference between binding and unbinding (dissociation time) is measured for forward (disruption of ZF1) and reverse (disruption of ZF3) unzipping. (C) Mean dissociation time, calculated for forward and reverse unzipping. Data shown as mean ± s.e.m., n = 25 and 14. ***P < 0.001, two-sample Student’s t-test.