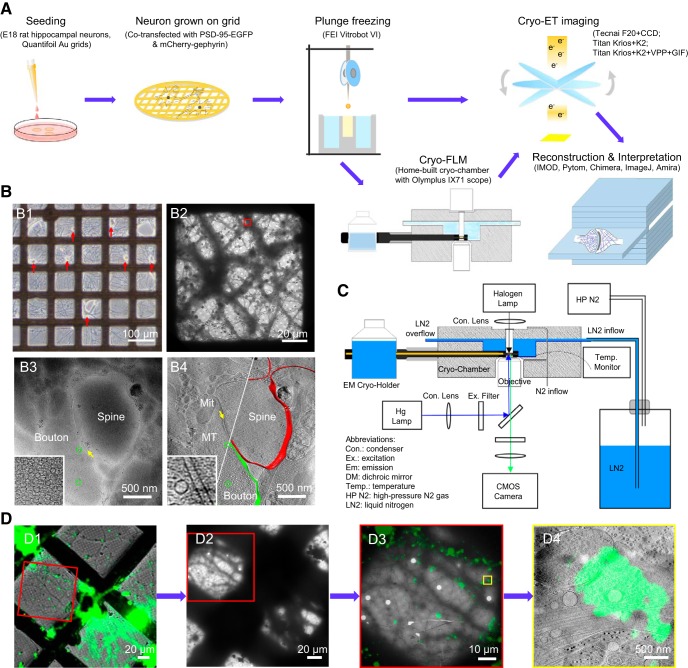
Figure 1.
Imaging primary rat hippocampal neurons with cryo-ET/cryo-CLEM. A, Illustration of the workflow of cryo-ET/cryo-CLEM imaging of neurons grown on gold EM grids. B, Representative results from different stages of the workflow. B1, LM image of cultured neurons (red arrows indicate cell bodies). B2, Cryo-EM image of neuronal processes in one grid square. B3, A single cryo-EM projection image of the boxed area in B2 showing a synapse-like structure with a presynaptic bouton (Bouton) containing a dense population of SVs (green circles), a postsynaptic spine (Spine), and a relatively uniform cleft (yellow arrow). Inset shows a zoomed-in view of the synaptic bouton area with a dense population of SVs. B4, A tomographic slice showing fine structure of the same synapse in B3, which was identified as a spine synapse by following through the tomogram in 3D, with mitochondrion (Mit), microtubules (MT), and SVs (green circles) and superposed with segmented presynaptic membrane (green) and postsynaptic membrane (red). Inset shows a zoomed-in view of the synaptic cleft area with transcleft structures. C, Schematics depicting main components of cryo-fluorescence light microscope with an EM cryo-holder. D, Pipeline of imaging synapse with cryo-CLEM. D1, Merged cryo-fluorescence and cryo-bright-field light images. D2, Low-magnification cryo-EM image including the same grid square. D3, Merged images of boxed area in D1 and D2 after fine alignment. D4, Tomographic slice of the boxed area in D3 superimposed with aligned fluorescence image showing the structure of a synapse with a green fluorescent punctum.