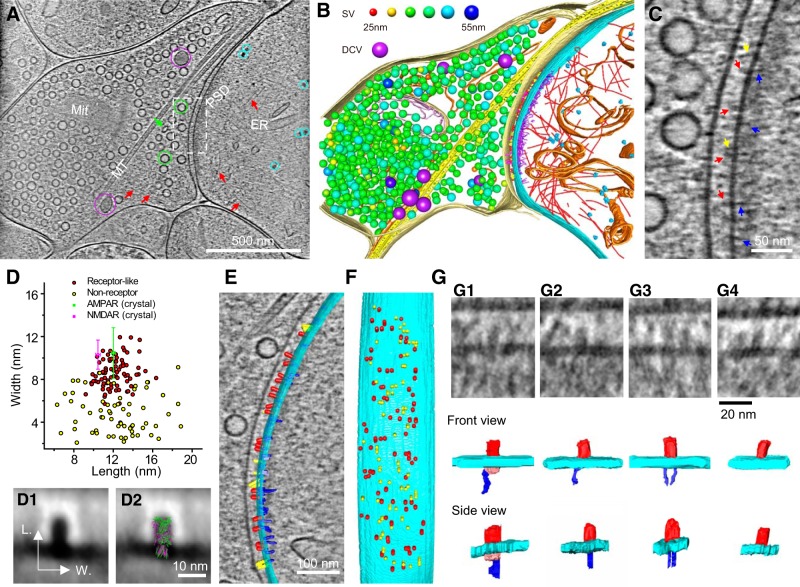
Figure 8.
Putative receptors and scaffolding proteins in an excitatory synapse. A, An 8.7-nm-thick tomographic slice of an excitatory synapse. Circles: SVs (green), DCVs (purple), ribosome-like structures (cyan); arrows: ellipsoidal vesicle (green), putative actin filaments (red). ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; Mit, mitochondria; MT, microtubule. B, 3D segmented structures of the whole tomogram (∼300 nm thickness) of the same synapse shown in A rendered as surfaces, colored as follows: outer-Mit, gold; inner-Mit, light pink; MT, yellow; ER, orange; ribosomes, cyan; actin filaments, red; presynaptic membrane, light yellow; postsynaptic membrane, cyan; presynaptic putative adhesion molecules, magenta; postsynaptic putative adhesion molecules, yellow; putative glutamate receptors, red; PSD filaments attached to the postsynaptic membrane, blue; PSD filaments away from the postsynaptic membrane, purple. Except for DCVs (purple), the size of SVs was color-coded (top). The same code also applies to Figure 9 and Movies 2–5. C, Zoomed-in view of the dashed-box area in A with arrows pointing to putative proteins on the postsynaptic membrane: glutamate receptors, red; other cleft structures, yellow; PSD filaments, blue. D, Scatter plot of length and width dimensions of the particles on the postsynaptic membrane at the synaptic cleft side. Red dots are putative glutamate receptors, and yellow dots are putative nonreceptor structures identified by visual inspection. The sizes of putative receptors (length: 12.1 ± 1.4 nm; width: 8.6 ± 1.4 nm, n = 81) are similar to that of extracellular domains of the crystal structures of AMPAR (green; length: 12.0 ± 0.2 nm; width: 10.5 ± 2.4 nm) and NMDAR (magenta; length: 10.5 ± 0.2 nm; width: 10.3 ± 1.4 nm; see detailed calculation of averaged dimensions in Materials and Methods). D1, Averaged 2D image of all particles in the red cluster in D. D2, D1 with AMPAR (green) and NMDAR (magenta) superposed. E, F, Segmented structures on the postsynaptic membrane either superposed on a 1.54-nm-thick (gray) tomographic slice (E) or 90°-rotated (F) to reveal their deposition on the postsynaptic membrane (cyan). Structures were colored as follows: putative glutamate receptors, red; putative nonreceptor structures on the cleft side, yellow; putative scaffolding proteins on the cytoplasmic side, blue. G, Four types of glutamate receptor-like particles with their interactions on the cytoplasmic side. G1, NMDAR-like structure (extracellular domain: red) had a ∼10 nm globular cytoplasmic domain (pink), which linked to one filamentous structure (blue). G2, G3, AMPAR-like structures (extracellular domain; red) linked to one and two filamentous structures (blue). G4, AMPAR-like structure with no associated filamentous structure. The postsynaptic membrane in all four panels is shown in cyan.