Figure 9.
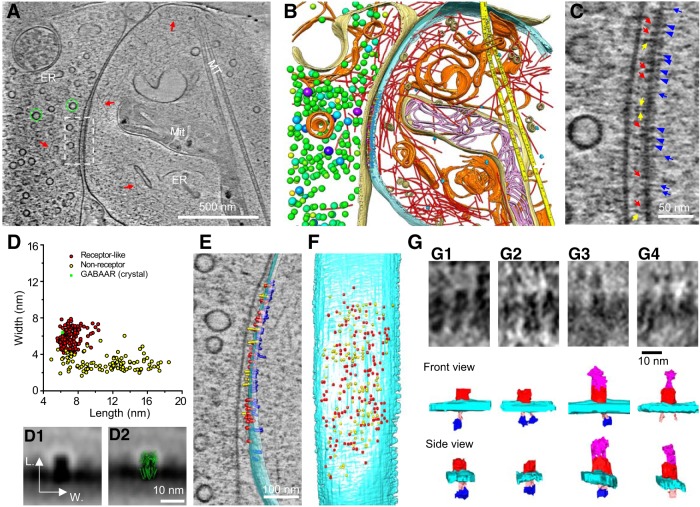
Putative receptors and scaffolding proteins in an inhibitory synapse. A, An 8.7-nm-thick tomographic slice of an inhibitory synapse. Green circles, SVs; red arrows, actin filaments; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Mit, mitochondria; MT, microtubule. B, 3D segmented structures of the whole tomogram (∼370 nm thickness) of the same synapse shown in A rendered as surface, colored the same as the labels in Fig. 8B except for postsynaptic vesicles (beige). C, Zoomed-in view of the dashed-box area in A with arrows and arrowheads pointing to particles attached to the postsynaptic membrane. Putative receptors, Red arrows; putative adhesion molecules, yellow arrows; short PSD particles, blue arrowheads; and long PSD particles, blue arrows. D, Scatter plot of length and width dimensions of the structures on the postsynaptic membrane at the synaptic cleft side. Red dots are putative GABAARs, and yellow dots are putative nonreceptor structures identified by visual inspection. The mean sizes of putative receptors (length: 7.1 ± 0.9 nm; width: 5.9 ± 0.9 nm, n = 143) are close to those of the extracellular domain of the crystal structures of GABAARs (green; length: 6.2 ± 0.1 nm; width: 6.4 ± 0.1 nm; see detailed calculation of averaged dimensions in Materials and Methods). D1, Averaged 2D image of all particles in the red cluster in D. D2, D1 with GABAAR (green) superposed. E, F, Segmented structures on the postsynaptic membrane either superposed on a 1.54-nm-thick (gray) tomographic slice (E) or 90° rotated (F) to reveal their position on the postsynaptic membrane (cyan). Putative GABAAR, Red; putative nonreceptor structures in the cleft, yellow; putative scaffolding proteins, blue. G, Typical GABAAR-like structures and their interactions at cytoplasmic and cleft side. GABAAR-like structures (extracellular domain: red) each linked to one or two hammer-like structures, which had a dense “head” (blue) and a thin “neck” (pink), at cytoplasmic side (G1–G3). Some of GABAAR-like structures only linked to two “necks” (G4). Additionally, some of GABAAR-like structures were connected to putative adhesion molecules (magenta) in the extracellular side (G3, G4).