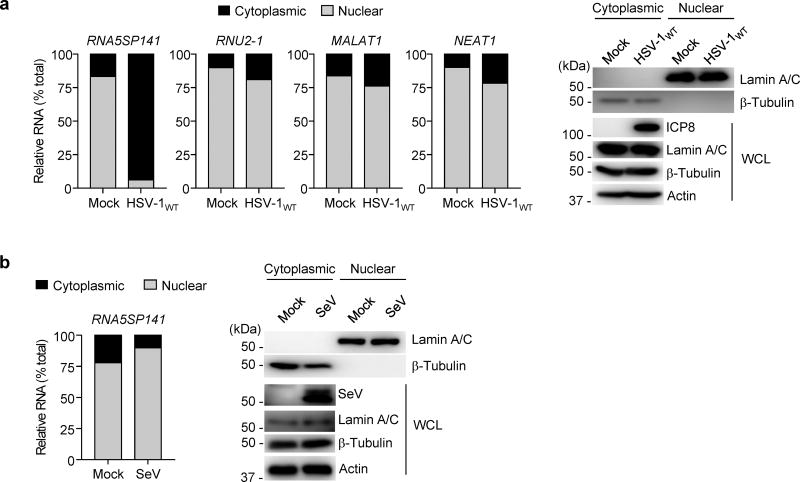
Figure 3.
RNA5SP141 is relocalized from the nucleus to the cytoplasm during HSV-1 infection. (a) Left: Relative abundance of RNA5SP141 transcripts in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of HEK 293T cells that were infected with HSV-1WT (MOI 1) for 16 h, or left uninfected (Mock), determined by cytoplasmic-nuclear fractionation assay and qRT-PCR. Analysis of the relative abundance of RNU2-1, MALAT1, and NEAT1 RNA served as controls. Right: IB analysis of Lamin A/C and β-Tubulin confirmed the purity of the nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction, respectively. IB analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) with anti-HSV-1 infected cell protein 8 (ICP8) and anti-actin served as infection and loading controls, respectively. Left margin, size in kilodaltons (kDa). (b) Left: Relative abundance of RNA5SP141 transcripts in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of HEK 293T cells that were infected with SeV (50 HAU/ml) for 16 h or left uninfected (Mock), determined by fractionation assay and qRT-PCR analysis as described in (a). Right: IB analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions as in (a). IB analysis of WCL with anti-SeV confirmed efficient infection. Data are representative of two independent experiments.