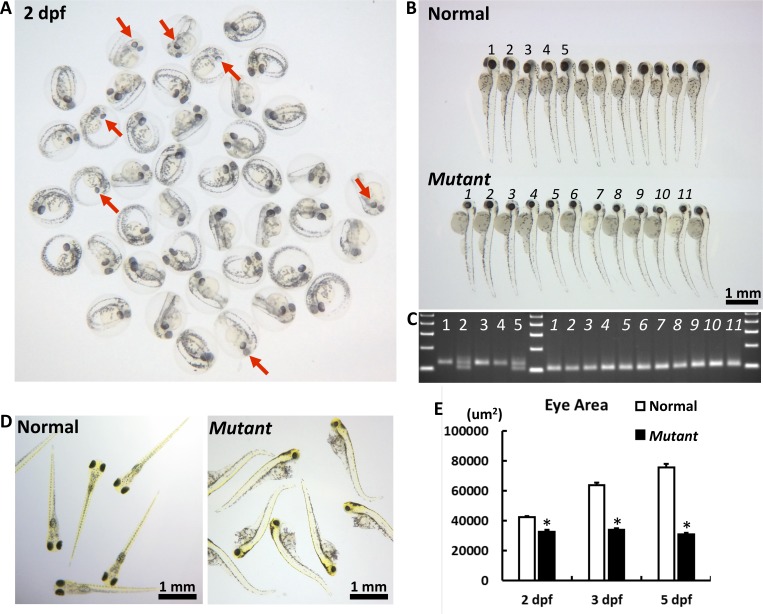
Figure 2.
The macroscopic eye phenotype of the cct2-L394H-7del mutant. (A) The representative picture of F3 embryos from F2 cross mating at 2 dpf. At this stage, some embryos had smaller eyes with reduced pigmentation (marked by red arrows) compared with most embryos. (B) The representative picture of F3 embryos from F2 cross mating at 3 dpf. At this stage, the homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant embryos (lower row) were easily distinguished from wild-type and heterozygous cct2-L394H-7del embryos (upper row) by smaller size and circular shape of their eyes. The numbering (1–5 for normal eye and 1–11 for smaller eye larvae) is identical to the numbering in (C). (C) The genotyping of embryos labeled in (B) by PCR. The wild-type allele produces a 125-bp band, while the mutant allele produces a 101-bp band. (D) The representative picture of F3 embryos from F2 crossmating at 5 dpf. At this stage, wild-type and heterozygous larvae start to swim, while homozygous mutant larvae are not able to swim. (E) Comparison of the eye area between normal versus homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant embryos at 2, 3, and 5 dpf. *P < 0.05.