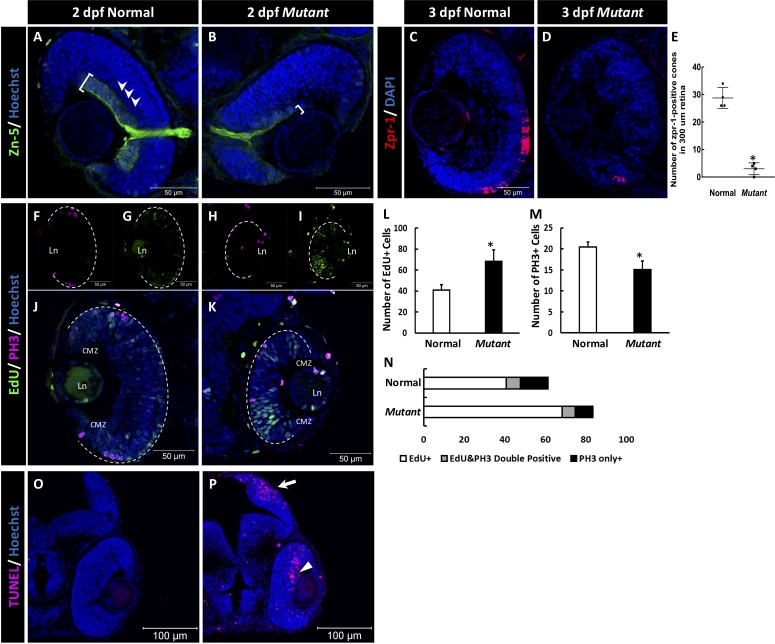
Figure 3.
The retinal phenotype of the homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutants at 2 pdf. (A, B) Staining of wild-type (A) and homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant (B) retinas with antibodies against Zn-5. Note a dramatic reduction of Zn-5 staining of the retinal ganglion cell layer (marked by a white bracket) and thinner optic nerve in cct2-L394H-7del mutant compared with wild-type. The lamination of the neural retina was more pronounced in wild-type embryos than in mutants. (C, D) The cone photoreceptor was underdeveloped in the homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutants at 3 dpf. Staining of wild-type (C) and homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant (D) retinas with antibodies against zpr-1. (E) Quantification of zpr-1–positive cells in wild-type and homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant retinas (n = 4). (F–I) The distribution of PH3-positive and EdU-positive cells in the retina. In wild-type embryos, PH3-positive cells (F) and most of EdU-positive cells (G) were found in the ciliary marginal zone and the area of neuronal precursors localization. In the retina of homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutants, PH3-positive cells were found in the ciliary marginal zone, area of neuronal precursors localization and lens epithelium (H). EdU-positive cells were found through the neural retina, in the ciliary marginal zone and lens epithelium (I). The white dashed lines indicate the eyecup boundaries. (J–K) Merged images of EdU and PH3 staining of the retina of wild-type (J) and homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant (K). (L–N) Quantification of EdU-positive, PH3-positive, and EdU/PH3-double positive cells in wild-type and homozygous cct2-L394H-7del mutant retinas (n = 10). (O, P) TUNEL staining of wild-type (O) and mutant (P) retinas. Arrow marks the optic tectum, the area of retinal ganglion cell axon projection; arrowhead marks TUNEL-positive cells in the neural retina. CMZ, ciliary marginal zone; Ln, lens. Scale bars: 50 μm. *P < 0.05.