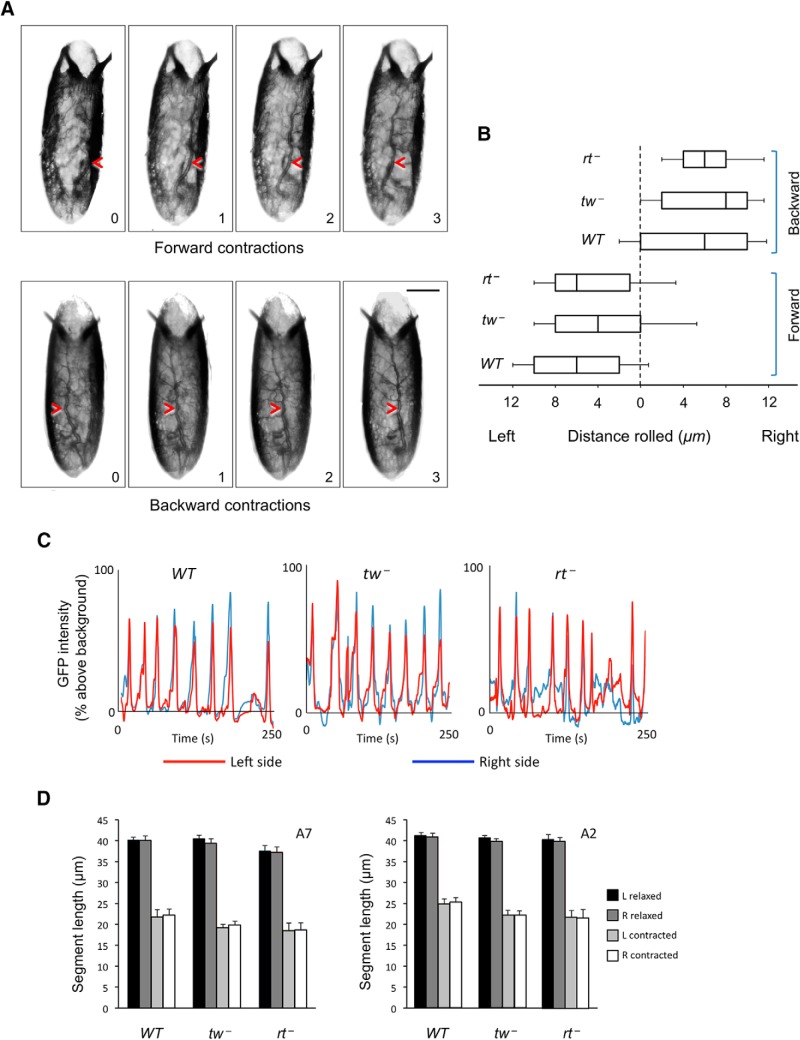
Figure 2.
Embryos roll chirally inside their shells during peristaltic contractions. A, Time series of rolling during consecutive forward and backward contractions. Rolling is obvious from changes in the position of a dorsal trunk trachea (red arrowhead). Scale bars, 100 μm. B, Quantification of the average distance rolled during backward and forward contraction waves in WT, tw−, and rt− embryos, as measured from halfway between anterior and posterior ends. Boxes represent the interquartile range, lines represent the median values, and error bars are SEs of the mean. No significant difference was detected among genotypes for either forward or backward rolling. Number of embryos and contractions analyzed (for each type of contractions): 10 embryos and at least 45 contractions per genotype for WT and tw−, and 5 embryos and at least 21 contractions for rt −. C, D, Mutant embryos do not have left-right contraction asymmetry. C, Examples of contraction waves progressing along the left and right sides of the embryo in WT, tw−, and rt− genotypes with MHC-GFP expression, shown as graphs of GFP intensity over time. In all genotypes, contractions occur largely simultaneously on right (blue line) and left (red line) sides. Although amplitude of individual left-side and right-side contraction peaks may be slightly different, either the left or right peak can be bigger or smaller without noticeable bias, and similar differences in individual waves are present in wild-type as well as mutant embryos. D, Analysis of segment length at posterior (segment A7) and anterior (segment A2) regions in relaxed and contracted states indicates that neither the left nor the right side contracts more than the other in wild-type and mutant embryos on average. At least 5 embryos and 25 contraction waves per embryo were analyzed for each genotype. In all panels:WT, wild-type; rt−, rtP/rtP; tw−, tw1/ tw1 (or tw1/Y). Statistical analyses: B, p > 0.9 for differences among forward or among backward contractions; p < 2E-5 for comparison between forward and backward contractions. D, p > 0.9 for differences between left and right side contractions, calculated for each genotype.