Figure 4.
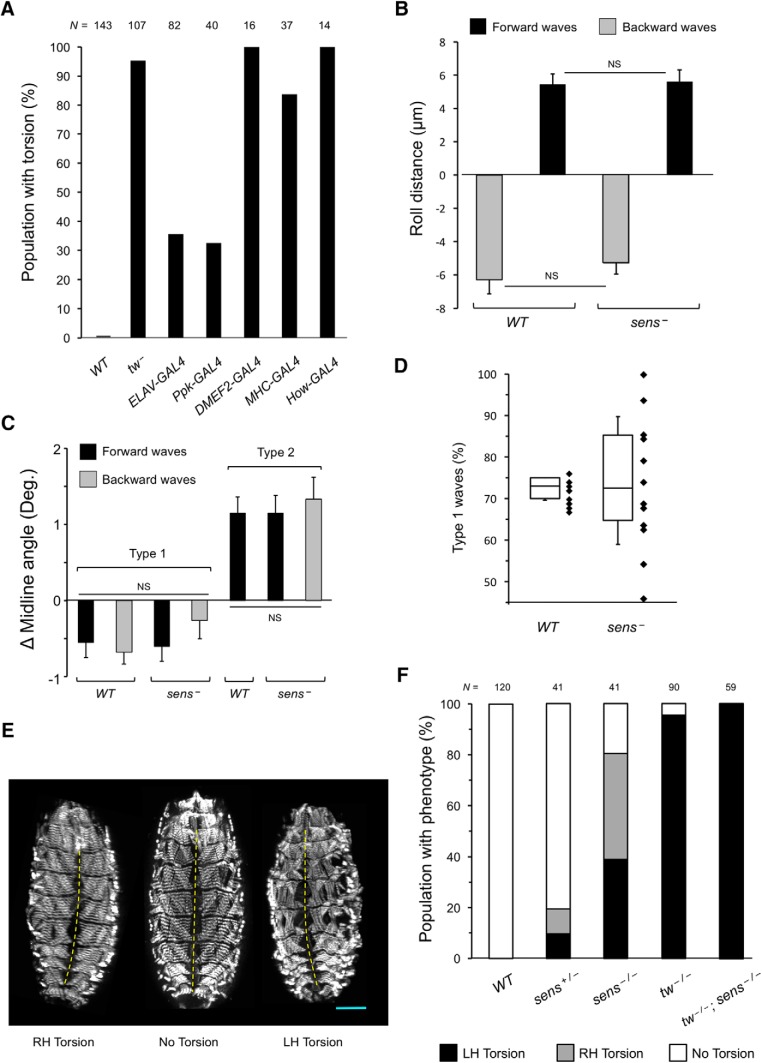
POMTs are required in peripheral sensory neurons for the maintenance of posture. A, Rescue of embryonic torsion by transgenic expression of UAS-tw construct in tw mutants using cell-specific drivers. Expression in all neurons (ELAV-GAL4) or in class IV da neurons (Ppk-GAL4) can substantially rescue torsion, while muscle-specific expression using DMEF2-GAL4, MHC-GAL4, and How-GAL4 cannot rescue the torsion phenotype (the presence of a driver or the UAS-tw transgene alone did not affect the torsion phenotype, which was confirmed in control experiments). Genotypes are designated as follows: WT, wild-type. tw−, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y). ELAV-GAL4, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y); UAS-tw/ELAV-GAL4. Ppk-GAL4, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y); UAS-tw/+; Ppk-GAL4 /+. DMEF2-GAL4, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y); UAS-tw/+; DMEF2-GAL4/+. MHC-GAL4, tw1/ tw1( or tw1/Y); UAS-tw/+; MHC-GAL4/+. How-GAL4, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y); UAS-tw/How-GAL4. B, Effect of forward and backward type 1 contractions on rolling in sens mutants compared with wild type. There is no significant difference between wild-type and sens mutants for corresponding waves (p = 0.98). C, Effect of type 1 and type 2 contractions on torsion in sens mutants. As in other genotypes, type 1 and type 2 waves result in negative (right-handed torsion) and positive (left-handed torsion) midline angles, respectively. In sens mutants, unlike any other genotype analyzed, a significant number of type 2 backward contractions were observed. Similar to type 2 forward waves, these also resulted in left-handed torsion. There were no significant differences between groups of data within a given contraction type (p > 0.05). D, Although WT and sens− embryos generate a similar proportion of type 1 waves on average, sens mutants have a much greater variability in the proportion of type 1 waves between individual embryos (black diamonds), suggesting that some embryos should develop body torsion. E, Examples of sens mutants with left-handed (LH) or right-handed (RH) body torsion, or without body torsion phenotype. F, Proportions of embryos with left-handed torsion, right-handed torsion, and no detectable torsion among WT, sens−, tw−, and tw−; sens− double mutants. N, Number of embryos analyzed for each genotype. All panels: WT, wild-type. Sens−, sensE2. Tw−, tw1. tw−/−; sens−/−, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y); sensE2/sensE2. Corresponding wild-type alleles are indicated by “+.” Unless indicated otherwise, at least 12 embryos and 15 contractions per embryo were assessed for each genotype. Statistical analyses: C, p > 0.9 for differences among data for same contraction type, p < 1E-5 for differences between type 1 and type 2 contractions, all genotypes. D, p = 0.97.