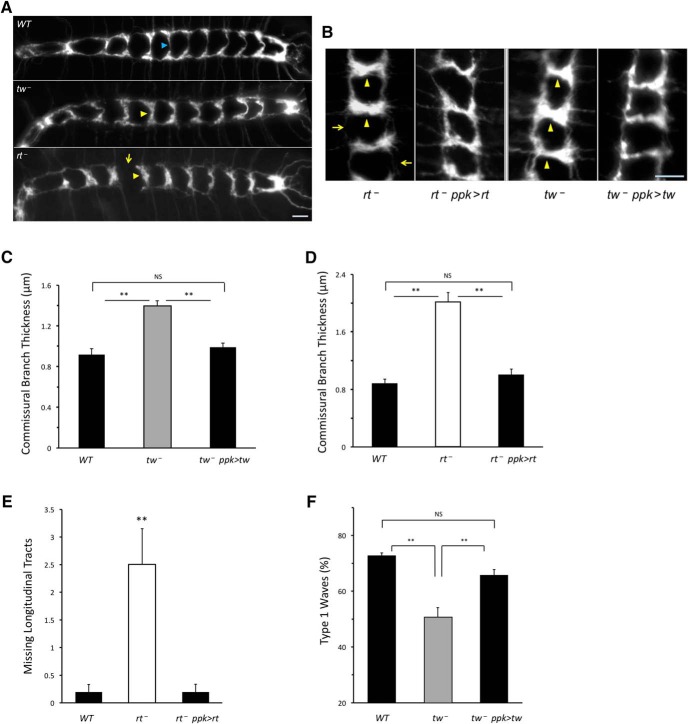
Figure 5.
POMTs affect the function of peripheral sensory neurons. A, POMT mutants have abnormal axonal projections of class IV da sensory neurons in the ventral ganglion. The laminar pattern of axonal projections shows abnormally thickened commissural tracts in rt and tw mutants (yellow arrowheads, compared with tracts indicated by blue arrowheads in WT control), and missing longitudinal tract in rt mutants (arrow). B–F, Transgenic expression of POMTs in class IV da neurons can rescue the phenotype of axonal projections (B–E) and abnormal pattern of contraction waves (F). B, Representative images of the same region of the laminar pattern (neuromeres a1–3 that are more frequently affected in POMT mutants) are shown for mutant and rescue genotypes. The phenotypes of thickened commissural branches (arrowheads) and depleted longitudinal tracts (arrows) are rescued by transgenic expression of POMTs in class IV da neurons. Number of animals analyzed for each genotype: WT, 14;tw−, 15;tw−, ppk>tw (rescue), 14 (C);WT, 10;rt−, 10; rt−, ppk>rt (rescue), 11. (D–E). Number of contractions (embryos) analyzed in F: WT, 186 (10);tw−, 163 (10);tw−, ppk>tw (rescue), 128 (8). In all panels, error bars indicate SEM. **p < 0.01; ns, not significantly different. WT, wild-type. tw−, tw1/tw1(or tw1/Y). tw−; ppk>tw, tw1/ tw1(or tw1/Y); Ppk-GAL4/+; UAS-tw/+. rt−, rt2/rt2. rt−, ppk>rt, rt2 Ppk-GAL4/rt2 UAS-rt. Driver-only and UAS-transgene-only control genotypes were also analyzed for corresponding rt and tw mutant alleles and found to be indistinguishable from mutants alone. Axonal projections were visuaized with Ppk-tdGFP (Han et al., 2012). Anterior is to the left (A) or up (B). Scale bar, 10 μm. Statistical analyses: C–F, p values for differences between WT and mutant, rescue and mutant, and between WT and rescue genotypes, respectively: 4E-5, 3E-4, 0.79 (C); 6E-9, 4E-8, 0.62 (D); 1E-3, 8E-4, 0.98 (E); 1E-6, 4E-4, 0.18 (F).