Figure 6.
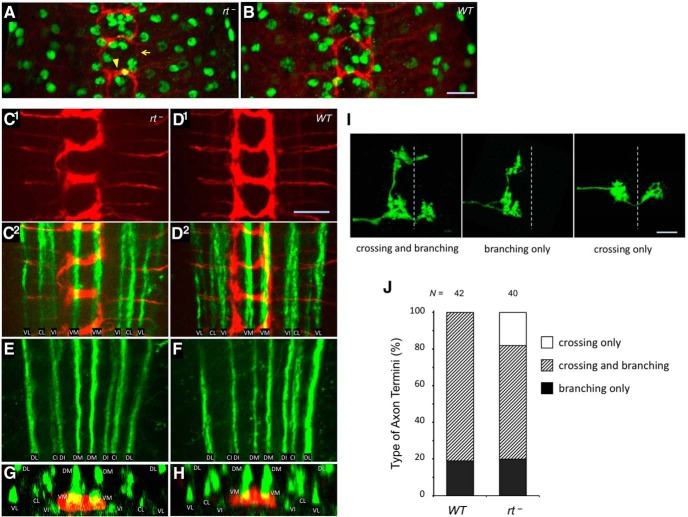
POMT mutations do not generally affect glia development and axon pathfinding, while being associated with defects in patterning of sensory axon termini. A, B, Immunostaining with anti-Repo antibody that specifically labels glial cells (green) revealed no significant defects in the distribution and number of glial cells in rt mutants (22.1 ± 0.9 and 23.7 ± 0.8 glial cells per hemisegment in rt− and WT control, respectively; t test, p > 0.2). C–F, FasII-positive long axon tracts in the ventral ganglion appear normal in rt mutants. C1, D1, Class IV sensory axons (red) in rt− and wild-type control, respectively. C2, D2, overlay of the axon staining shown above (C1, D1) with the staining of long axonal tracts (FasII, green) in the ventral part of the ganglion. The same region of the ventral ganglion corresponding to neuromeres a1–3 is shown for both genotypes. E, F, FasII immunostaining of long axonal tracts in dorsal part of the ganglion in rt− and wild-type, respectively. G, H, Z-projections reconstructed from stacks of horizontal optical sections through the ventral ganglion show similar dorsoventral lamination of class IV axon termini (red) in rt− and wild-type, respectively, based on their location relative to FasII tracts (green). The commissural branch of neuromere a2 is shown for both genotypes. I, Examples of individual class IV sensory axons with “crossing and branching,” “branching only,” and “crossing only” types of morphology, relative to the midline (dashed line). J, Quantification of types of class IV sensory axons revealed by Flp-out clones in wild-type and rt mutants. N, Number of individual axons analyzed. Nomenclature of FasII tracts is according to the study by Landgraf et al. (2003): C, central; D, dorsal; I, intermediate; L, lateral; M, median; V, ventral. Axons were visualized using Ppk-tdTom (A–H; Han et al., 2012) or Flp-out technique (I, J; see Materials and Methods). Images in C–F represent projections of stacks of optical sections through ventral and dorsal regions of the ventral ganglion, respectively. rt−, rt2/rt2. Scale bar, 10 μm.