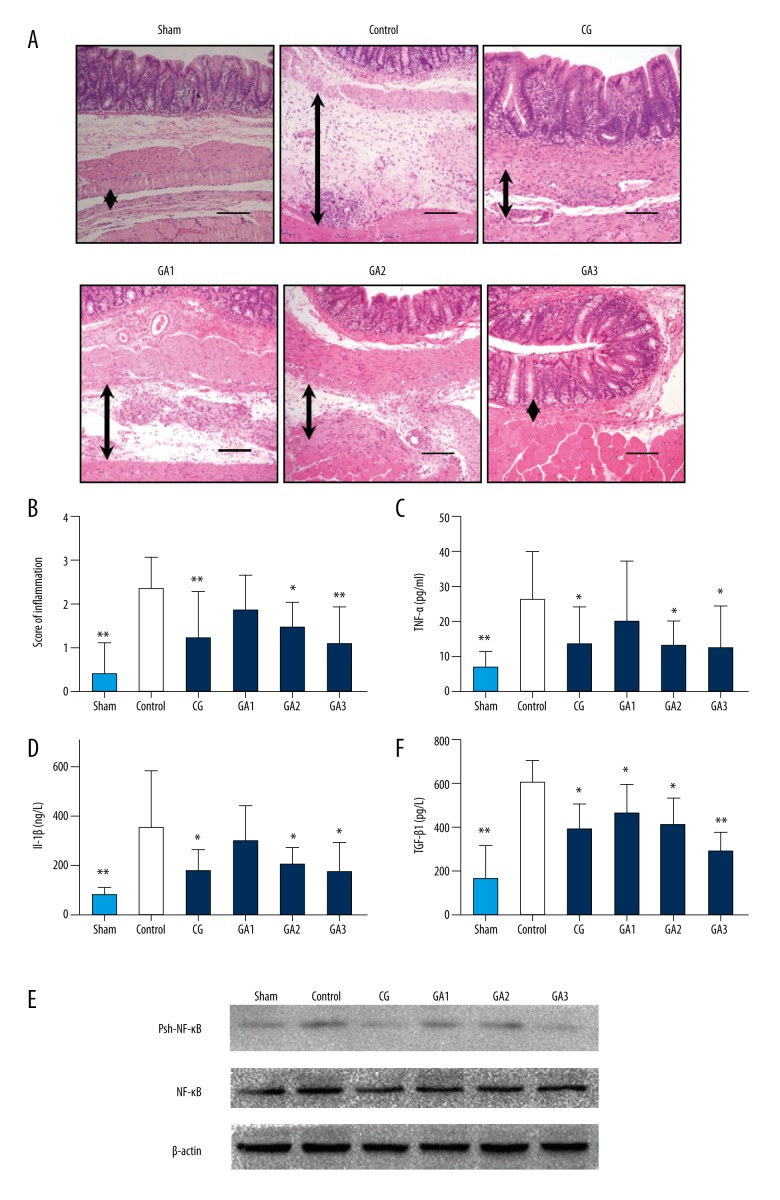
Figure 2.
Higher doses of gallic acid treatment can reduce the inflammation in the adhesion tissue in the rat model on the 7th postoperative day (n=8; compared with the control group, * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01). (A) HE staining of each group at 100× magnification. The black arrows indicate tissue with adhesion. (B) The inflammatory score of each group based on HE staining (compared with the control group, * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01, abnormal distribution, Kruskal-Wallis test). (C) TNF-α expression in each group (compared with the control group, * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01, abnormal distribution, Kruskal-Wallis test). (D) Expression of IL-1β in each group (compared with the control group, * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01, abnormal distribution, Kruskal-Wallis test). (E) TGF-β expression in each group (compared with the control group, * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01, abnormal distribution, Kruskal-Wallis test). (F) Western blot detection of NF-kB and phosphorylated NF-κB expression in each group.