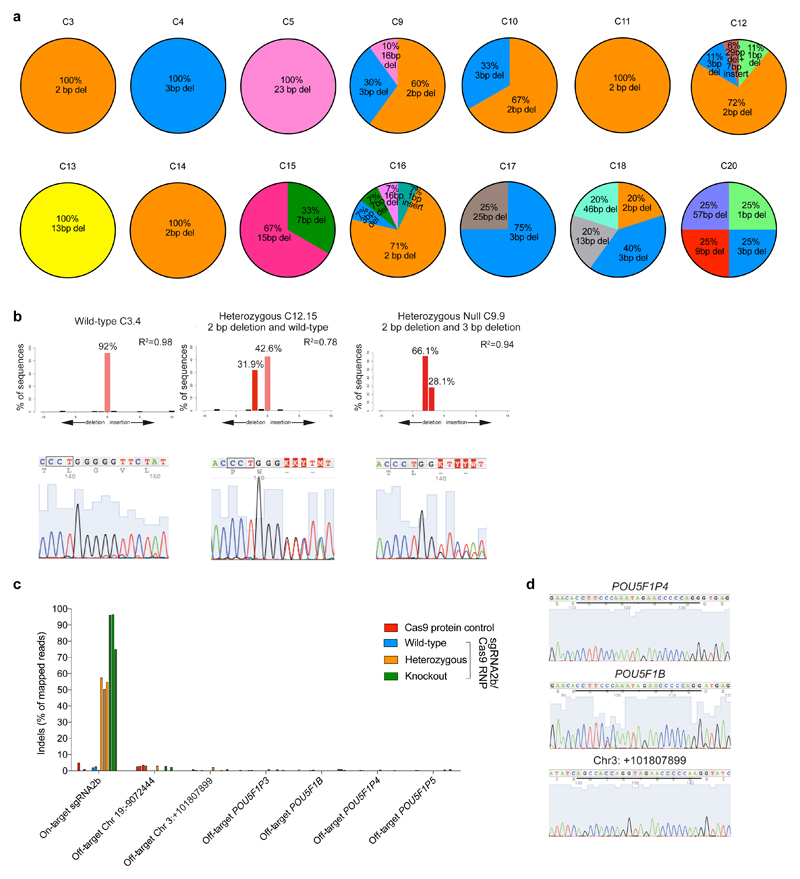
Extended Data Figure 7. Evaluating on-target and putative off-target mutations in human embryo cells.
a, The type and relative proportion of indel mutations observed compared to all observable indel mutations within each human embryo. b, Quantification of indels by TIDE analysis. Representative plots and Sanger sequencing chromatograms are shown from OCT4-null, heterozygous and wild-type human cells. c, Percentage of indel mutations detected at the sgRNA2b on-target site and putative off-target sites in single cells microdissected from Cas9 protein-microinjected control blastocysts or blastocysts that developed following sgRNA2b–Cas9 complex microinjection. Putative off-target sites were evaluated in cells that were previously determined to be OCT4-null (green), heterozygous (orange) or wild-type (blue) along with samples from Cas9 protein-microinjected embryos (red). Three representative examples of wild-type and edited cells are shown. d, Sanger sequencing chromatograms from OCT4-null single cells collected from human blastocysts that developed following sgRNA2b–Cas9 microinjection. The chromatograms exemplify the sequence detected in all of the other samples analysed. Underlined is the sequence of the putative off-target site.