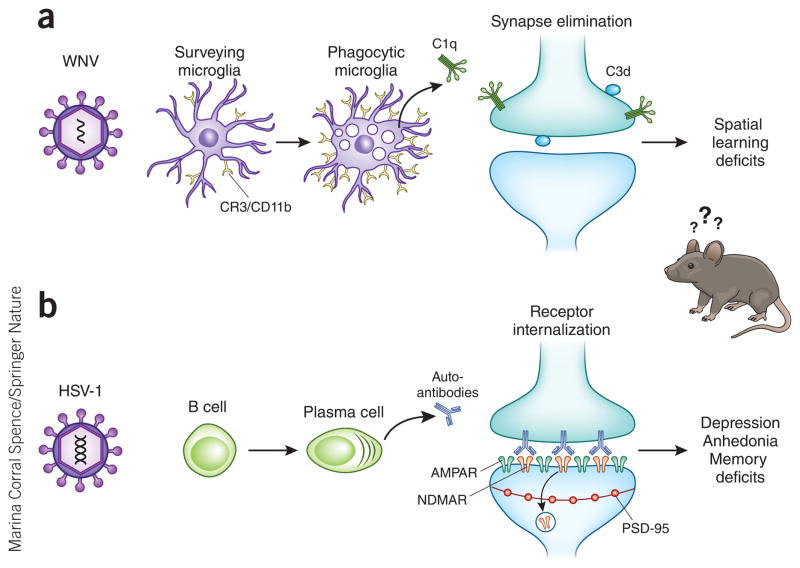
Figure 3.
Mechanisms underlying neurological sequelae in a subset of viral encephalitis survivors. (a) Microglia are activated after WNV infection, leading to upregulation of complement receptor 3 (CR3) and expression of complement component C1qa. C1qa and the downstream complement cleavage protein C3d localize to presynaptic terminals in the hippocampus. Complement-mediated engulfment of tagged synapses by microglia leads to selective loss of presynaptic terminals in the CA3 region of the hippocampus and deficits in spatial learning. CD11b, cluster of differentiaton 11b. (b) B cells can produce autoantibodies to synaptic proteins, including NMDAR, after HSV-1 mediated encephalitis. Autoantibodies bind to NMDAR on the post-synaptic terminal, which leads to selective internalization of NMDAR, whereas other synaptic components, such as AMPAR and PSD-95, remain intact. Loss of NMDAR in the hippocampus leads to behavioral memory deficits and neuropsychiatric symptoms of depression and anhedonia.