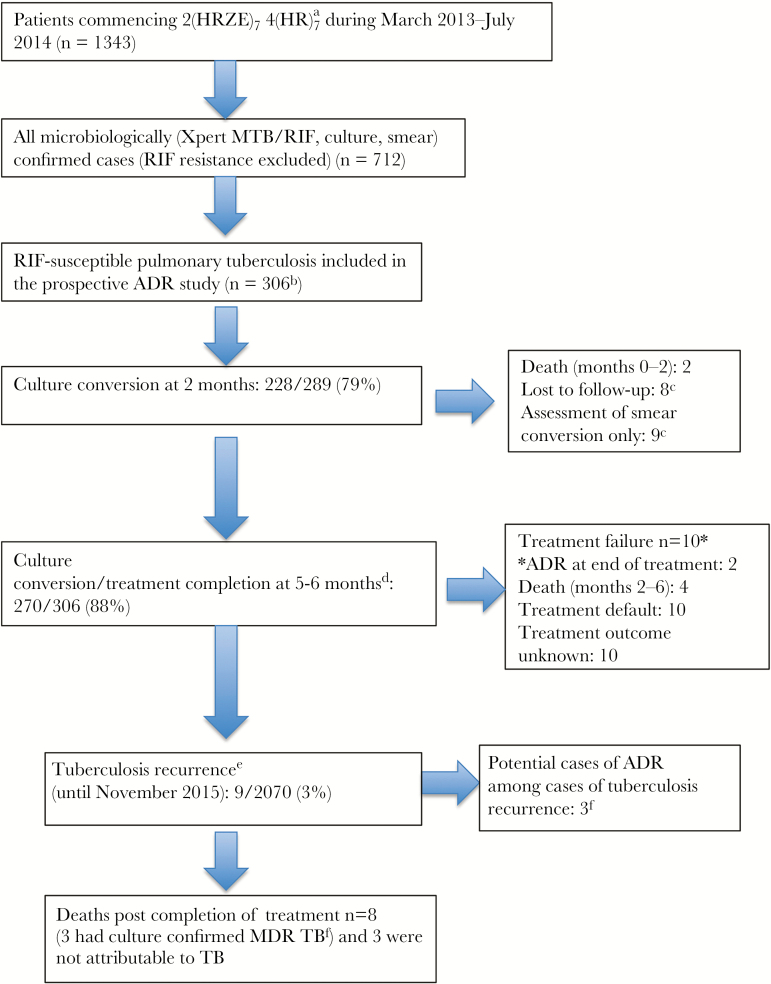
Figure 1.
Study recruitment and participant outcomes. aThe regimen consisted of a 2-month initial phase of a daily fixed-dose combination of isoniazid, rifampicin (RIF), pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, following by a 4-month continuation phase of a daily fixed-dose combination of isoniazid and RIF. bReasons why patients were not recruited to the acquired drug resistance (ADR) study were as follows: (1) they had received ≥3 doses of tuberculosis treatment (includes individuals were transferred in from other clinics/hospitals and those who started treatment on days the study team was not recruiting), (2) they declined participation or were unable to provide informed consent, (3) they were unwilling to undergo human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing, and (4) they were unable to expectorate sputum. cParticipants were not included in the denominator. dA total of 240 participants had assessment of culture conversion at the end of treatment. A further 40 were assessed as treatment completers or underwent assessment of smear conversion. eEight recurrences were either culture confirmed and/or smear positive (grading, 2+/3+ [definite recurrence]). One of these recurrences was symptomatic, scanty smear positive, and had a confirmatory Xpert MTB/RIF test revealing RIF susceptibility (possible recurrence). fFindings are for the same 3 individuals. Abbreviation: MDR, multidrug resistant.