Figure 2.
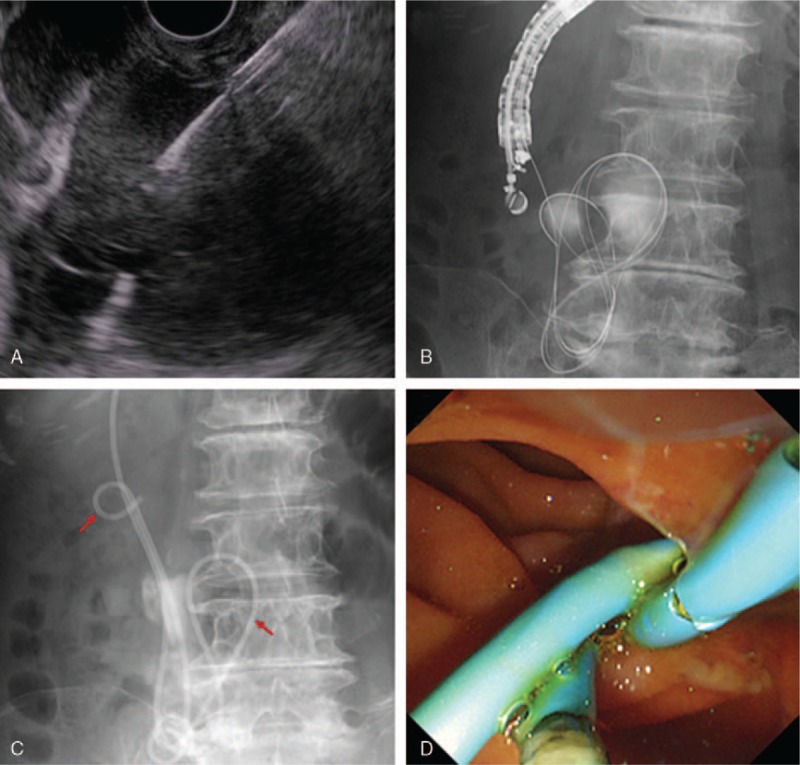
EUS-guided idiopathic retroperitoneal abscess drainage with internal and external stent placement. After confirming that there was almost no blood flow along the path of the needle by Doppler, we performed needle puncture via the descending portion of the duodenum using a 19-gauge needle. Then, we passed a 0.025-inch guidewire into the abscess, inserted, a double-lumen catheter, and placed another guidewire. After expanding the fistula with an 8.5-Fr wire-guided diathermic dilator, we placed a 7-Fr, 10 cm double-pigtail stent (left red arrow) and 7-Fr, 250 cm endoscopic nasobiliary drainage (ENBD) tube (right red arrow). D, Under endoscopy, the internal stent and ENBD tube were placed via a duodenal fistula into the abscess. Infected fluid was seen draining out of the stent and fistula into the duodenum by endoscopy. EUS= endoscopic ultrasound.
