Table 1. Biological activity of R848 covalently coupled to the NHS ester end of 7 different amide-sulfhydryl crosslinkers.
R848-linker compounds were produced commercially with the exception of the R848-SM(PEG)4 compound (indicated by a star), which was produced in-house and was used to construct the original IPR8 vaccine (IPR8-SM(PEG)4-R848). Raw264 cells were stimulated with 10 μM R848-linker compounds for 24 hrs and TNFα production was measured. Controls: no stimulation: 6.7±5.7 pg/ml; R848.NH2: 6867±1611pg/ml. Results shown are the mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. Differences in TNFα production of R848-linker compounds as compared to SM(PEG)4-R848 or as compared to R848-NH2 were not significant by one-way ANOVA analysis with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
| R848-linker compound | spacer arm | length | TNFα (pg/ml) | Spacer arm structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML2-102-1 | BMPS | 5.9Å | 9481 ± 3440 |
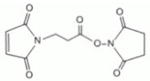
|
| ML2-103-1 | GMBS | 7.3Å | 8970 ± 3065 |

|
| ML2-104-1 | EMCS | 9.4Å | 4595 ± 1566 |
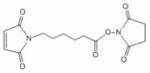
|
| MAL-PEG2-1 | SM(PEG)2 | 17.6Å | 7985 ± 2639 |
|
| MAL-PEG4-1* | SM(PEG)4 | 24.6Å | 7236 ± 1526 |
|
| MAL-PEG8-1 | SM(PEG)8 | 39.2Å | 5938 ± 2706 |
|
| MAL-PEG16-1 | SM(PEG)16 | 65.3Å | 5906 ± 2437 |
|
