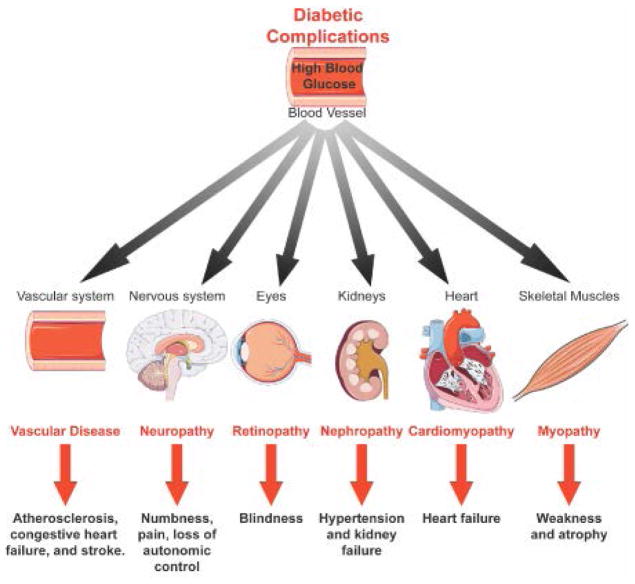
Figure 2. Systemic complications of diabetes.
Diabetes increases the risk for coronary artery disease, which can block blood flow and cause heart attack and/or stroke 3, 4. Hyperglycemia damages nerve fibers causing neuropathies that can adversely affect the digestive tract, urinary tract, heart and blood vessels 5–7. Retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in diabetic adults 7–9. Almost half of diabetic patients develop diabetic nephropathy 5–7. In most cases, patients develop kidney failure requiring dialysis 6. Under diabetic conditions, heart muscle structure and function are impaired leading to cardiomyopathy 15, 16. Diabetes also impacts skeletal muscle function causing muscle weakness and atrophy 13, 14.