Figure 4. Absence of ufmylation induces inflammatory signaling and ER stress.
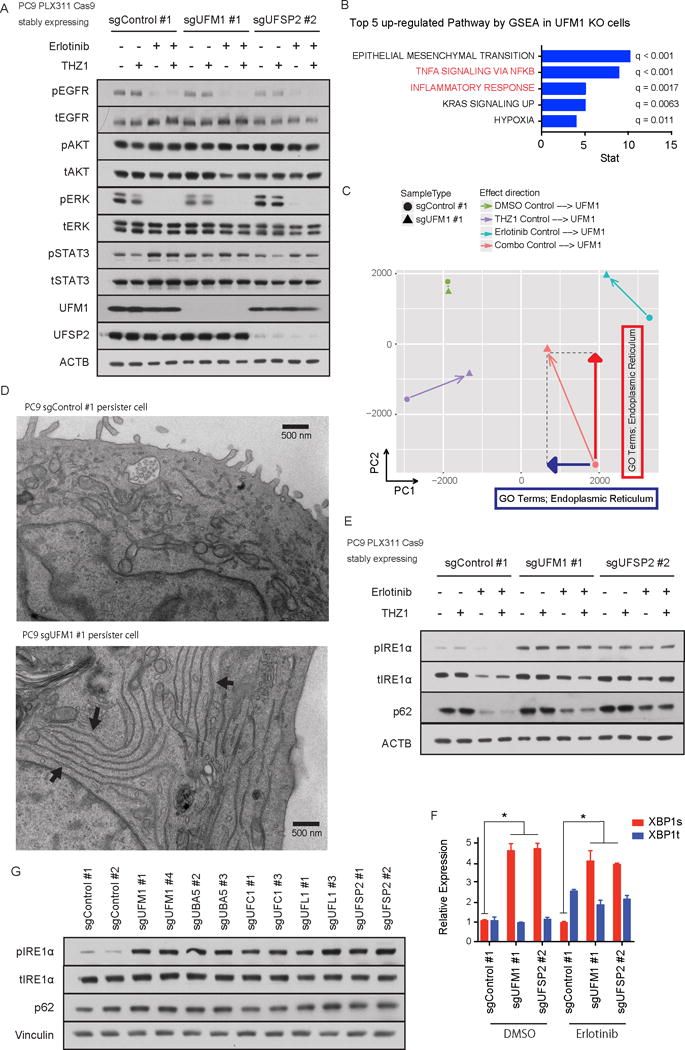
A) Immunoblotting of EGFR signaling pathway components. UFM1 or UFSP2 depleted PC9 cells or control PC9 cells were treated with DMSO, 50 nM THZ1, 100 nM erlotinib (Erlotinib) or 50 nM THZ1 plus 100 nM erlotinib (Combo) for 72 hr. B) Top 5 up-regulated pathways in UFM1 knock out PC9 cells compared with Control PC9 cells analyzed by GSEA analysis. C) Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed for average FPKM values of each condition and resulting PCA scores were used. GO term analysis was performed against each principal component and ER GO terms were highly ranked with the indicated directions. D) Representative pictures of electron microscopic experiments. Each arrow in UFM1 KO persister cells indicates accumulation of abnormal ER. E) Immunoblotting of unfolded protein response pathway components in UFM1 or UFSP2 depleted or control PC9 cells. Cells were incubated with DMSO, 50 nM THZ1, 100 nM erlotinib (Erlotinib) or 50 nM THZ1 plus 100 nM erlotinib (Combo) for 72 hr. F) qRT-PCR of spliced or total XBP1 in PC9 cells after 100 nM erlotinib treatment. PC9 cells were transduced with indicated sgRNAs. Each bar indicates mean ± SD. G) Immunoblotting analysis of ufmylation pathway genes in PC9 cells transduced with indicated sgRNAs.
