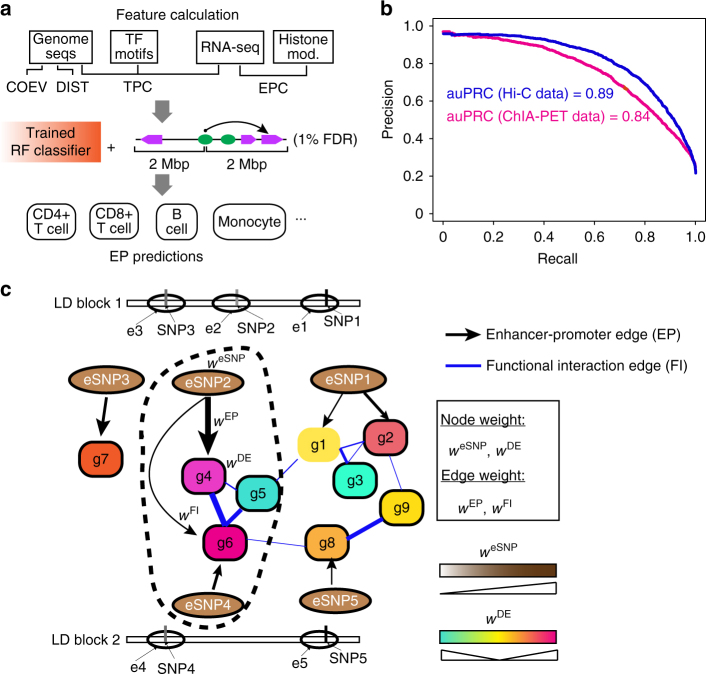
Fig. 1.
Construction of weighted and disease-relevant gene regulatory network for prioritizing risk SNPs located in regulatory DNA sequences. a The IM-PET algorithm for predicting enhancer targets. Features used by the random forest (RF) classifier are: COEV, coevolution of enhancer and target promoter; DIST, distance constraint between enhancer and target promoter; TPC, transcription factor and target promoter correlation; EPC, enhancer and target promoter profile correlation; FDR, false discovery rate. b Performance evaluation of IM-PET using Hi-C and ChIA-PET data. Sources of Hi-C and ChIA-PET data are listed in Supplementary Table 2. c Schematic for an integrated, disease-relevant gene regulatory network. The network involves SNP-containing enhancers and their target genes and functional interactions among the target genes. Such a network is constructed by integrating transcriptomic and epigenomic data on cells/tissues relevant to the disease under study. The encircled subnetwork represents pathways targeted by a candidate risk eSNP. LD, linkage disequilibrium; e, enhancer; g, gene; EP, enhancer−promoter interaction; FI, functional gene interaction; eSNP, enhancer SNP; WeSNP, weights for eSNPs; WDE, weights for differential gene expression; WEP, weights for EP edges; WFI, weights for FI edges