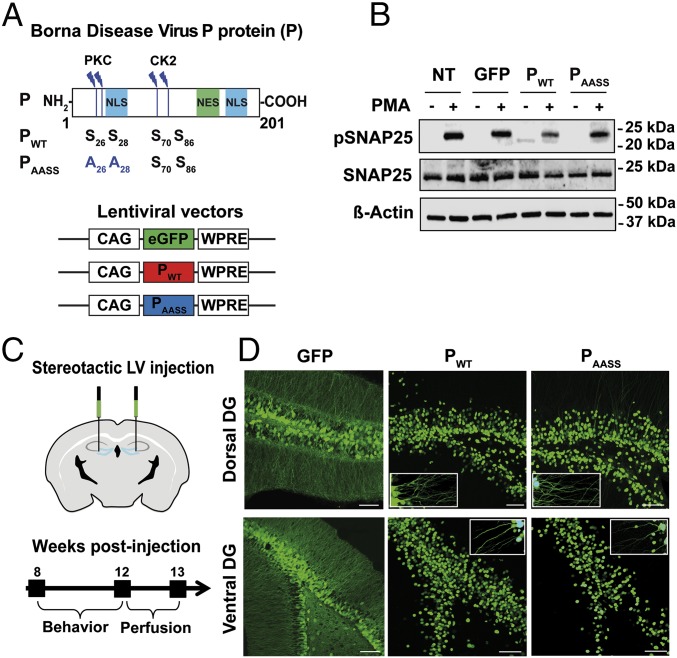
Fig. 1.
Lentiviral expression of the P protein interferes with PKC-dependent phosphorylation in mouse hippocampal neurons. (A) Schematic representation of the P protein, displaying the protein kinase C (PKC) and casein kinase II (CK2) phosphorylation sites. NES, nuclear export sequence; NLS, nuclear localization sequence. Map of the lentiviral vectors (LVs) expressing GFP, wild-type P (PWT), or mutant P (PAASS). Also shown are: positions of the cytomegalovirus enhancer/chicken β-actin (CAG) promoter and woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE). (B) Western blot analysis of phospho-SNAP25 levels upon PKC stimulation. Protein extracts were prepared from neurons transduced with LVs expressing GFP (as a control), PWT, or PAASS, after stimulation or not with PMA. Nontransduced (NT) neurons were also processed in parallel. Levels for β-actin and total SNAP25 were used to normalize phosphorylation levels. Data shown are those of a representative experiment out of four that gave similar results. (C) Stereotaxic procedure for in vivo LV delivery and experimental timeline. (D) Expression of GFP, PWT, or PAASS in the DG of mice, 4 mo after surgery. Representative pictures of brain sections expressing GFP, PWT, or PAASS in the dorsal and ventral DG. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Insets show enlarged view to visualize P expression in the dendrites.