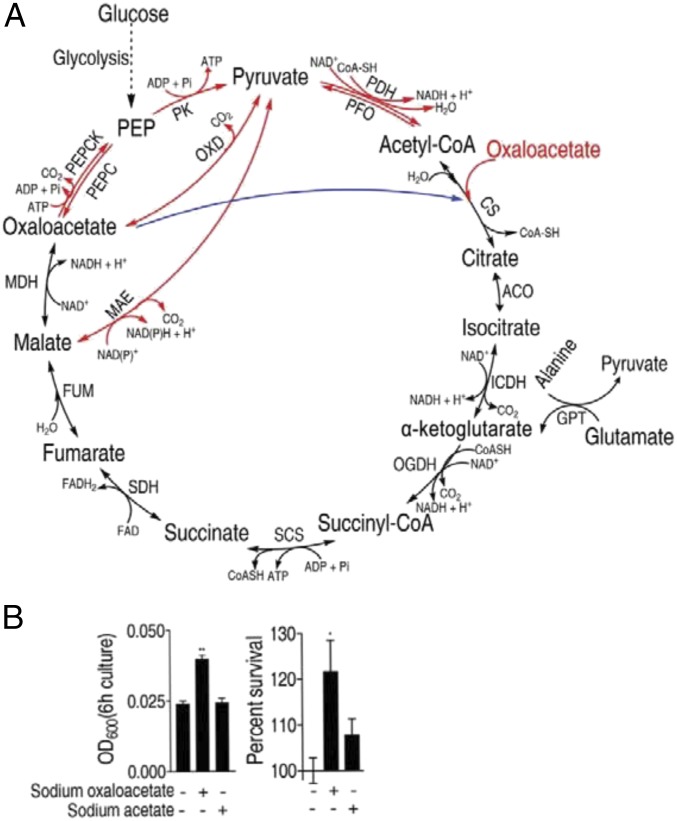
Fig. 2.
The P cycle and the TCA cycle in E. tarda. (A) Overview of the P cycle. Black line, overlapped pathway between the P cycle and the TCA; blue, a step of the TCA cycle, which does not exist in the P cycle; and red, pathways of the P cycle, which do not exist in the TCA cycle. ACO, aconitase; CS, citrate synthase; FUM, fumarase; GPT, glutamic-pyruvic transaminase; ICDH, isocitric dehydrogenase; MAE, malic enzyme (NAD-dependent malic enzyme and NADP-dependent malic enzyme); MDH, malate dehydrogenase; OGDH, α-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; OXD, oxaloacetate decarboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PEPC, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PFO, pyruvate-flavodoxin oxidoreductase; PK, pyruvate kinase; SCS, succinyl-CoA synthetase; and SDH, succinic dehydrogenase. (B) Optical density (OD) (Left) and percent survival (Right) of EIB202. Cells were grown in LB medium and then incubated in M9 medium with acetate (10 mM) or oxaloacetate (10 mM). Result (B) is displayed as mean ± SEM; at least three biological repeats were carried out. Statistically significant values are indicated with asterisk (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) and determined by Student’s t test.