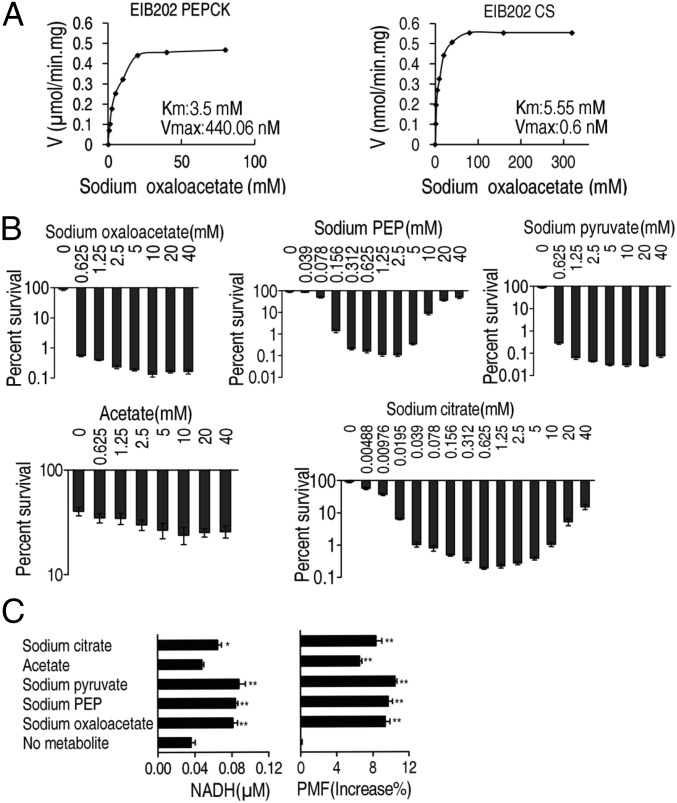
Fig. 3.
Oxaloacetate favors PEPCK to citrate synthesis, and the P cycle generates more NADH and PMF than the TCA cycle in E. tarda. (A) Michaelis–Menten kinetics of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and citrate synthase (CS) in oxaloacetate (0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 mM and 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320 mM, respectively). Cells were grown in LB medium and then incubated in M9 medium with acetate (10 mM). (B) Percent survival of EIB202. Cells were grown in LB medium and then incubated in M9 medium plus acetate (10 mM) in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of metabolites plus kanamycin (30 μg/mL). (C) NADH and PMF of EIB202. Cells were grown in LB medium and then incubated in M9 medium plus acetate (10 mM) in the presence or absence of the indicated metabolites sodium citrate (0.625 mM), sodium pyruvate (10 mM), sodium PEP (1.25 mM), or sodium oxaloacetate (10 mM). Result (B and C) is displayed as mean ± SEM, and three biological repeats were carried out. Significant differences are identified (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) as determined by Student’s t test. P < 0.01 in B except for acetate.