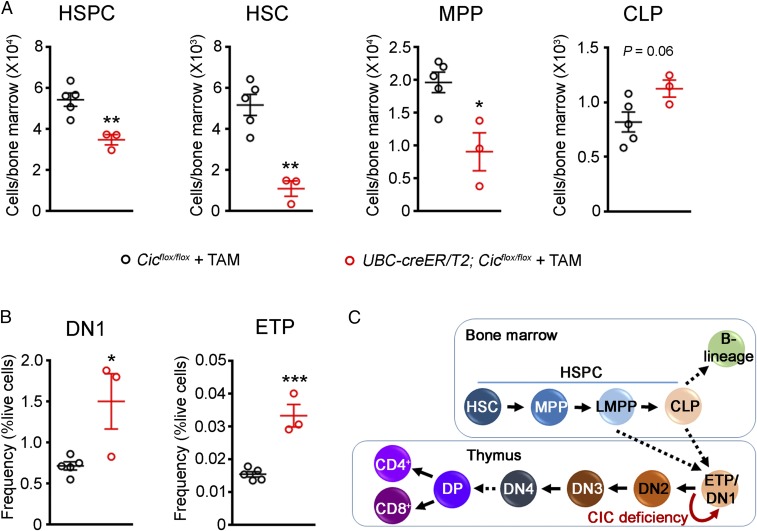
Fig. 3.
Loss of CIC disrupts the homeostasis of progenitor cells and alters early T cell development. (A) Analysis of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs, lineage− c-Kit+ Sca-1+; HSC, lineage− c-Kit+ Sca-1+ CD150+ CD48−; MPP, lineage− c-Kit+ Sca-1+ CD150− CD48−; and CLP, lineage− c-Kit+ Sca-1+ IL7Ra+) in Cicflox/flox and UBC-cre/ERT2; Cicflox/flox mice 2 wk posttamoxifen treatment (n = 3–5 animals). (B) Analysis of DN1 (CD4− CD8− CD44+ CD25−) and ETP (CD4− CD8− CD44+ CD25− c-Kit+) populations in Cicflox/flox and UBC-cre/ERT2; Cicflox/flox mice 2 wk posttamoxifen treatment (n = 3–5 animals). (C) Diagram showing progenitor cell development in the bone marrow and T cell development in the thymus. CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; DN, double negative; DP, double positive; ETP, early T cell precursor; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; HSPC, hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell; LMPP, lymphoid-primed multipotent progenitor; MPP, multipotent progenitor. Data are presented in scatterplots with error bars representing mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using two-tailed unpaired t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.