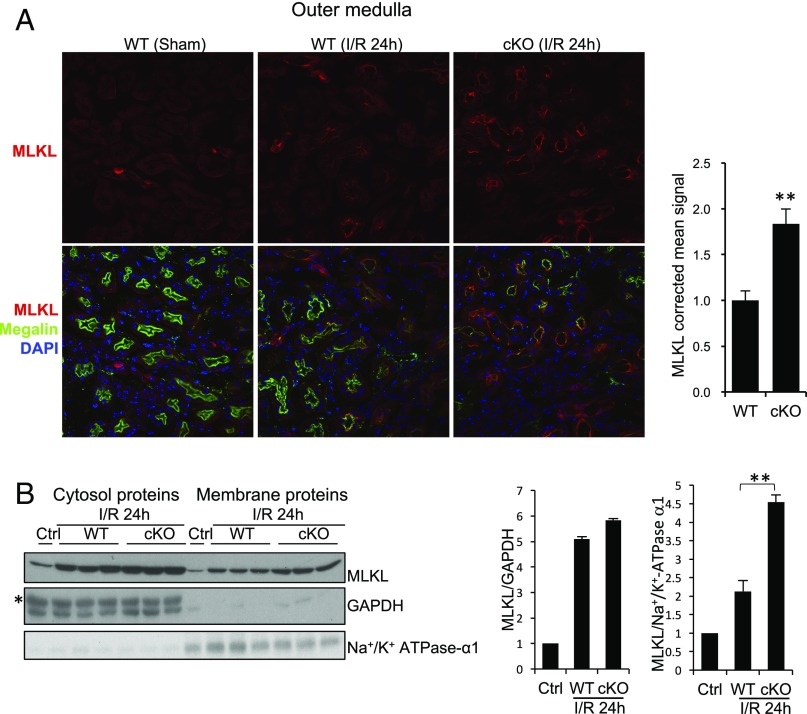
Fig. 3.
Cellular localization of MLKL in WT and Rgmb cKO kidneys after IRI. (A) MLKL localization in the outer medulla. Immunofluorescence was performed on sections from sham-operated kidneys and kidneys of WT and Rgmb cKO mice 24 h after ischemia (40 min) and reperfusion for MLKL. Costaining with megalin was included to identify proximal tubules. Outer medulla is presented. MLKL apical signal was quantified by ImageJ. Five mice were used for each group for MLKL quantification. (B) MLKL levels in cytosolic and membrane fractions of kidneys. Membrane proteins and cytosolic proteins were isolated from the cortex and outer medulla of control kidneys or kidneys of WT and Rgmb cKO mice with IRI, and subjected to Western blotting for MLKL (Left). MLKL relative to GAPDH in cytosolic fractions and MLKL relative to α1-subunit of Na+/K+ ATPase in membrane fractions were quantified by densitometry (Right). GAPDH was used as the loading control for cytosolic samples, and α1-subunit of Na+/K+ ATPase was used as the control for membrane proteins. **P < 0.01.