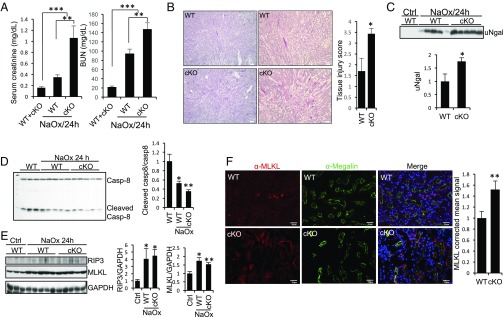
Fig. 4.
Tubule-specific ablation of Rgmb aggravates crystal cytotoxicity. Male WT and Rgmb cKO mice at 2 mo of age were injected (i.p.) with NaOx at 100 mg/kg body weight. Mice were killed after 24 h. (A) Serum creatinine and BUN levels in WT and Rgmb cKO mice injected without and with NaOx. (B) PAS staining of kidney sections from WT and Rgmb cKO mice after NaOx injection. Representative photographs at different magnifications show more brush border loss, tubular dilation, tubular cell depletion, and cast formation in Rgmb cKO mice than in WT mice. Quantitative assessment of tubular injury is presented. (C) Excreted Ngal in urine in WT and Rgmb cKO after NaOx injection. Urine samples were subjected to Western blotting for Ngal (Upper) and quantified by densitometry (Lower). (D) Cleaved caspase-8 levels in kidneys after NaOx injection. Kidney lysates collected 24 h after NaOx injection were subjected to Western blotting using an antibody that recognizes both full-length and Casp-8. Cleaved caspase-8 levels relative to full-length caspase-8 levels were quantified by densitometry. (E) Expression of RIP3 and MLKL in the kidneys of WT and Rgmb cKO after NaOx injection. Kidney lysates from WT kidneys and injured kidneys were subjected to Western blotting for RIP3 and MLKL. RIP3 and MLKL levels relative to GAPDH levels were quantified by densitometry. (F) Cellular localization of MLKL in the outer medulla of WT and Rgmb cKO kidneys after NaOx injection. Immunofluorescence was performed for MLKL (red). Costaining with megalin (green) was included to identify proximal tubules. Outer medulla is presented. MLKL apical signal was quantified by ImageJ. GAPDH was used as the loading control for Western blotting. n = 7 for A; n = 5 for B and F. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.