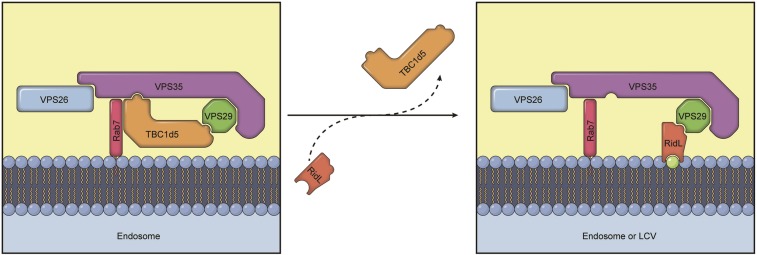
Fig. 6.
Model showing how RidL inhibits retromer-dependent transport. (Left) Retromer requires TBC1d5 for endosomal transport. TBC1d5 forms a tight complex with retromer through interacting both VPS35 and VPS29 and may function to regulate retromer assembly and turnover on endosomal membranes. Retromer cargoes, Sortin Nexins, VARP, and other known regulators are omitted for simplicity. (Right) During L. pneumophila infection or ectopic expression of RidL, RidL replaces TBC1d5. Upon ectopic expression of RidL, RidL is recruited to endosomes through interaction with VPS29 and endosomal lipid PtdIns(3)P (green dot). RidL replaces TBC1d5, and likely VARP, to block retromer-mediated trafficking. During L. pneumophila infection, retromer subunits are recruited to Legionella-containing vacuoles (LCVs) through their interaction with RidL and potentially other bacterial effector proteins.