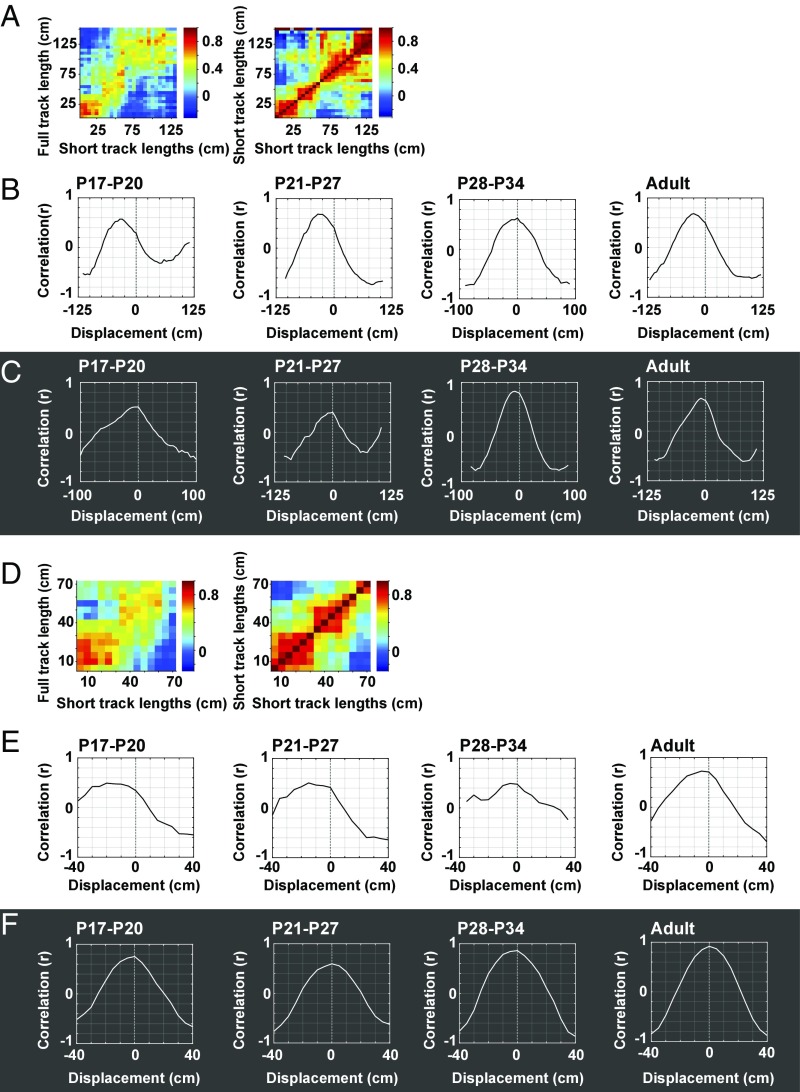
Fig. 6.
Displacement of cross-correlation matrix relative to autocorrelation matrix for rate maps on the short track. (A) Example rate maps on long vs. short track (Left) and corresponding autocorrelation matrix for the short track (Right). For the cross-correlation matrix (from Fig. 4), only the lower part, equivalent to the length of the short track, is shown, as only this part could have overlapping data, and could be correlated with, the autocorrelation matrix. Data shown are from the P17–P20 age group tested with lights off. (B) Comparison of cross-correlation and autocorrelation matrices for lights-on condition. For each trial, the cross-correlation matrix (lower, overlapping part) is shifted, bin by bin, relative to the autocorrelation. Line diagrams show correlations for successive horizontal shifts of the cross-correlogram. Negative displacement values indicate that maximum correlation is obtained by shifting the cross-correlogram in a left-to-right direction compared with the autocorrelogram. Note that, except for the P28–P34 group, the correlation peaks at negative displacement values, suggesting that place fields on the short tracks were shifted forward compared with the expected location if they depended only on the starting position. (C) Same as in B but with lights off. Maximum correlation was now obtained nearer the 0 position, suggesting that fields largely remained aligned to the start of the track. Alignment with the autocorrelogram was observed in all age groups. (D) Lower left quadrants of cross-correlation and autocorrelation matrices (bottom left parts of matrices in A). (E) Comparison of cross-correlation and autocorrelation matrices using a stepwise shift procedure as in B but now for the lower left quadrant of the matrices only. Lights were on. (F) Same as in E but with lights off. Maximum correlation for the lower left quadrant of the cross-correlation and autocorrelation matrices was observed with no displacement, confirming that fields remained largely aligned to the start position in darkness. Anchoring to the start position was observed during darkness in all age groups.