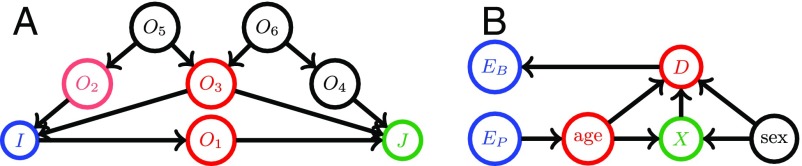
Fig. 2.
A is an example of a graphical causal model. The colored nodes are an example of a d-separation rule, where and are d-separated by . B is the graphical causal model for our CSF data analysis example. Here, the population characteristics difference only has a direct causal effect on the age distribution. The sample selection bias is only directly related to diagnosis status for each specific study. Nodes denoting age and sex influence the CSF measurements denoted by , which then influence the diagnosis status . The CSF measurements and the nodes and are d-separated by diagnosis status and age.