Figure 1.
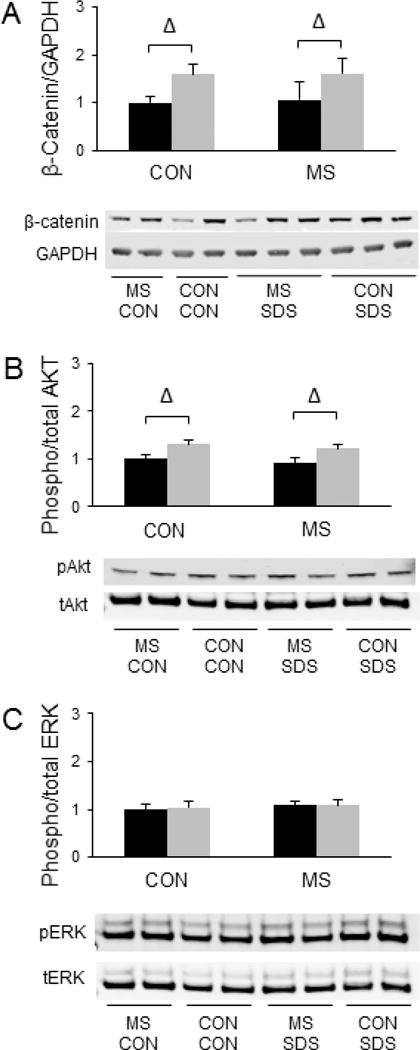
Combined effects of maternal separation (MS) stress and social defeat stress (SDS) on β-catenin levels in the nucleus accumbens compared to control (Con) animals. (A) Quantification and representative images for Western blot analysis of β-catenin/GAPDH levels in the nucleus accumbens. (B) Quantification and representative images for Western blot analysis of phosphorylated Akt/total Akt levels in the nucleus accumbens. (C) Quantification and representative images for Western blot analysis of phosphorylated ERK2/total ERK2 levels in the nucleus accumbens. Black bars show data from control mice not subjected to SDS; grey bars show data from mice exposed to SDS. Δ indicates significant main effect of SDS, p < 0.05. N = 10 per group.
