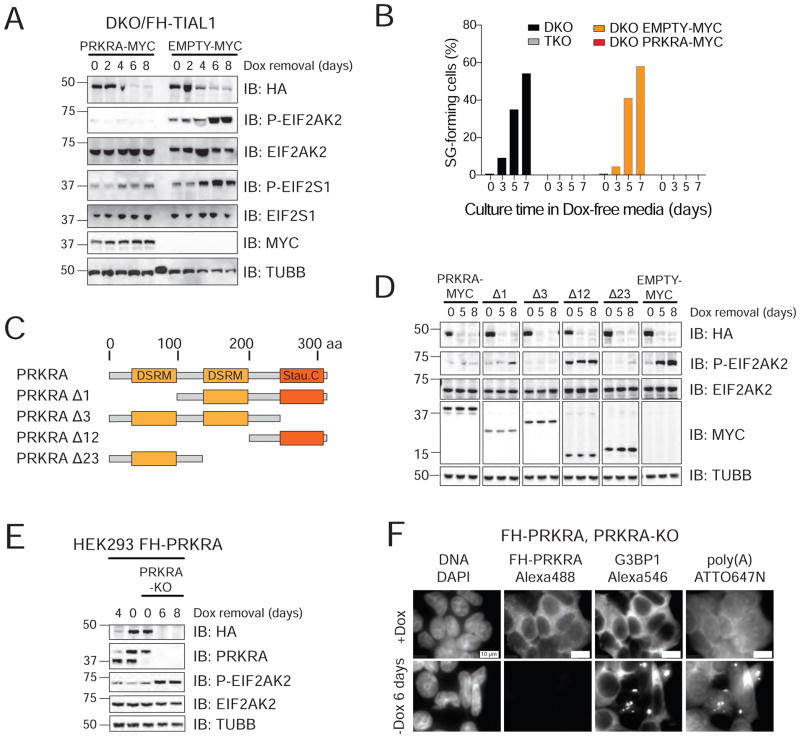
Figure 6. TIA1 proteins are essential for accurate PRKRA mRNA processing to prevent EIF2AK2 activation.
A) IB for phosphorylated EIF2AK2 and EIF2S1 on lysates of DKO/FH-TIAL1 cells expressing c-Myc-tagged PRKRA (PRKRA-MYC) or c-Myc alone (EMPTY-MYC) cultured with or without Dox. B) Proportion of SG-positive DKO/FH-TIAL1 and TKO/FH-TIAL1 cells as well as DKO/FH-TIAL1 cells either expressing PRKRA-MYC or EMPTY-MYC cultured as indicated. C) Domain organization of human PRKRA and truncated variants. DSRM, dsRNA-binding motif; Stau. C, Staufen C-terminal domain. D) IB for phosphorylated EIF2AK2 and EIF2S1 on lysates of DKO/FH-TIAL1 cells expressing PRKRA-MYC or c-Myc-tagged PRKRA mutants Δ1, Δ3, Δ12, Δ23 (as described in C) cultured with or without Dox. E) IB for phosphorylated EIF2AK2 on lysates of FH-tagged PRKRA expressing parental or PRKRA KO cells cultured with or without Dox. F) Localization of poly(A)-mRNAs as well as FH-tagged PRKRA and G3BP1 in FH-tagged PRKRA expressing PRKRA KO cells cultured with or without Dox by RNA-FISH and IF. Scale bar, 10 μm.