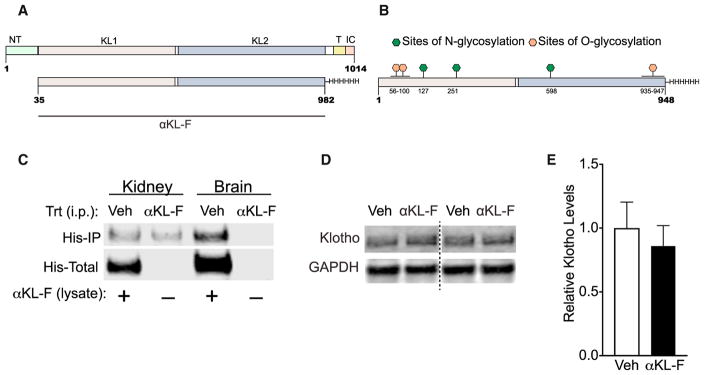
Figure 1. αKL-F Is a Recombinant Post-translationally Modified Fragment of Klotho, and Its Peripheral Administration Does Not Show BBB Crossing or Alteration of Endogenous Hippocampal Klotho Levels.
(A) Amino acid sequence of the endogenous α-klotho protein (top, aa 1–1014) and the recombinant α-klotho fragment (αKL-F, bottom, aa 35–982) followed by a His tag. N-T, N terminus; TR, transmembrane region; IC, intracellular domain.
(B) Locations of O-glycosylation and N-glycosylation sites of the recombinant protein made in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells.
(C) αKL-F was not observed to cross into the brain 4 hr following i.p. injection of Veh or αKL-F (100 μg/kg). Western blot shows immunoprecipitation against His-tagged αKL-F (His-IP) in kidney (detected) and brain (not detected) lysates. αKL-F was added to the veh-treated lysates as a positive control for detection of His-tagged protein (His-Total).
(D) Representative western blot showing Klotho and GAPDH levels in homogenized whole hippocampus 4–5 hr following Veh or αKL-F (i.p., 10 μg/kg) treatment (n = 12/group; male; age, 4 months). Images were captured from the same gel.
(E) Quantitation of endogenous brain klotho levels showing no differences between Veh- and αKL-F-treated mice. NTG levels are arbitrarily defined as 1.0.
Data are mean ± SEM.