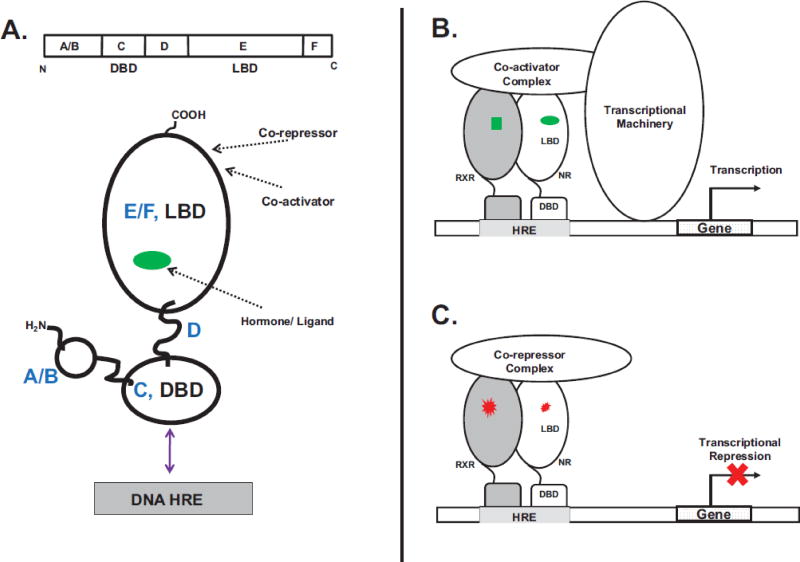
Figure 1. Nuclear Receptor (NR) Mode of Action and Molecular Topology.
A. The nuclear receptor topology and functional organization consists of distinct N-terminal A/B, a DNA-binding (C, DBD), linker D and C-terminal ligand-binding (EF, LBD) domains. Arrows show locations of the binding sites for ligand, co-activators/co-repressors and the DNA HRE. B. Ligand agonists (green) interact with the receptor (heterodimer of nuclear receptor (NR):retinoid X receptor, (RXR)). Ligand binding is accompanied by the recruitment of co-activators and the basal transcriptional machinery. C. In the absence of agonists or when bound to antagonists (red) the nuclear receptor is maintained in an inactive transcriptional state by co-repressor molecules.