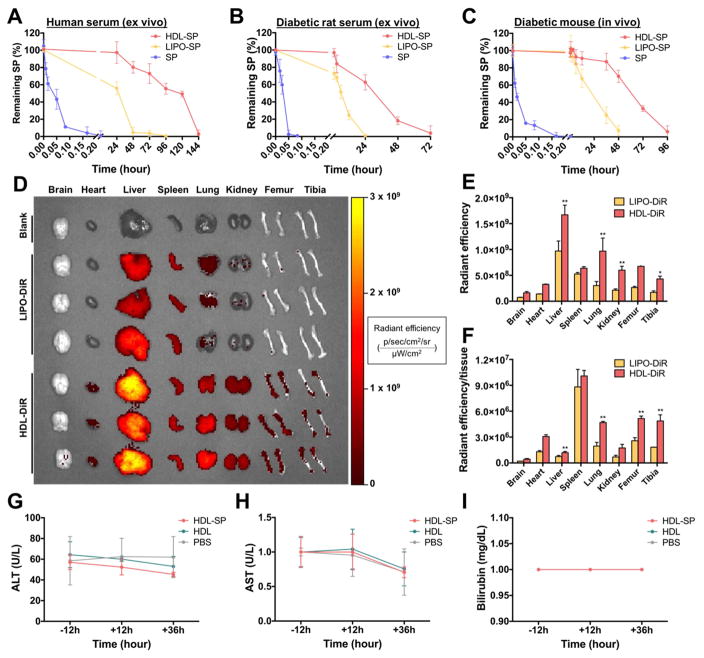
Figure 2. The pharmacokinetics and toxicity of HDL-SP nanodisc formulation.
Half-life of SP, LIPO-SP, and HDL-SP exposed to ex vivo condition of ((A) normal human serum and (B) diabetic rat serum. (C) In vivo half-life of SP, LIPO-SP, and HDL-SP at several time points after intravenous injection to diabetic mice. (D) Organ distribution of DiR-loaded liposomes (LIPO-DiR) or DiR-loaded HDL nanodiscs (HDL-DiR) 24 h after intravenous administration. Quantification of (E) total fluorescence intensity (p/sec/cm2/sr/μW/cm2) in each organ and (F) the fluorescence intensity normalized to tissue weight (p/sec/cm2/sr/μW/cm2/mg) in each organ (n = 3; **p < 0.01 versus each corresponding LIPO-DiR group). (G–I) Hepatotoxicity evaluation of HDL-SP nanodiscs on the base of the levels of (G) alanine aminotransferase (ALT), (H) aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and (I) bilirubin in serum collected from mice receiving intravenous injection of HDL-SP nanodiscs (n = 4).