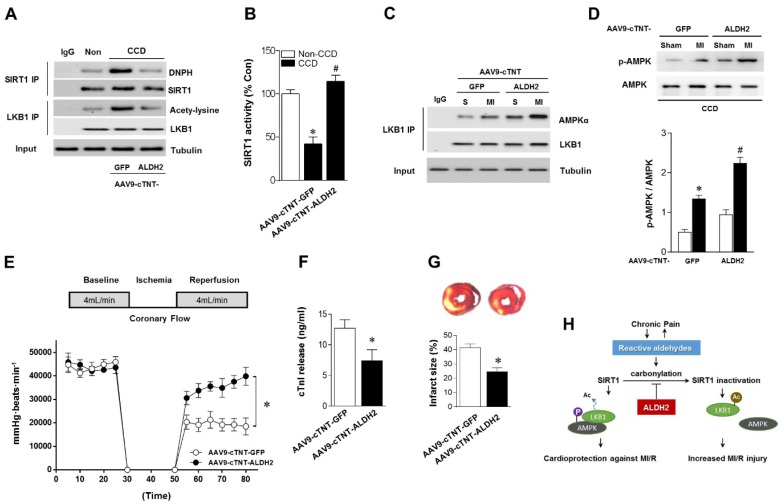
Figure 7.
Cardiac-specific ALDH2 upregulation in vivo ameliorates I/R injury in CCD mice. (A) Representative co-immunoprecipitation analysis of SIRT1carbonylation and LKB1 acetylation as well as (B) SIRT1 activity in the cardiac tissue from AAV9-cTNT-ALDH2-injected CCD mice or AAV9-cTNT-GFP-injected CCD mice compared to the no pain control mice; *P < 0.05 vs. no CCD control; #P < 0.05 vs. AAV9-cTNT-GFP-injected CCD mice. (C) Immunoblots of AMPKα from LKB1 immune-complexes and (D) immunoblots of p-AMPKα (Thr 172) during sham or ischemic conditions. Bar graphs show the ratio of phosphorylated to total AMPK; *P < 0.05 vs. AAV9-cTNT-GFP CCD sham; #P < 0.05 vs. AAV9-cTNT-GFP CCD ischemia. (E) Cardiac function shown by heart rate-LV pressure products and (F) Cardiac caspase-3 activity or (G) infarct size from AAV9-cTNT-ALDH2-injected CCD mice or AAV9-cTNT-GFP-injected CCD mice hearts subjected to 20 min global no-flow ischemia and 2 hours reperfusion; *P < 0.05 vs. AAV9-cTNT-GFP-injected CCD group. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 6 per group. (H) Summary of working hypothesis.