Table 1.
miRNA pairs cooperating in the regulation of E2F1.
| miRNA pair | miR-205-5pmiR-342-3p | miR-205-5pmiR-148a-3p | miR-205-5pmiR-377-3p | miR-205-5pmiR-148b-3p | miR-205-5pmiR-152-3p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary structure | 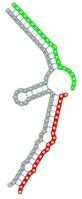 |
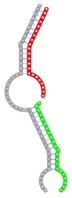 |
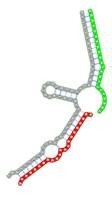 |
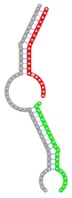 |
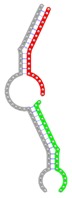 |
| Structure pattern | target self-complementarity | canonical triplex | target self-complementarity | canonical triplex | canonical triplex |
| Seed distance (nt) | 32 | 27 | 33 | 27 | 27 |
| ∆G (kcal/mol) | -50.56 | -45.26 | -44.86 | -44.66 | -42.76 |
| ∆∆G (kcal/mol) | -20.28 | -14.78 | -12.98 | -14.18 | -12.28 |
| Potential energy (kcal/mol) | -8241.33 | -7040.79 | -7623.90 | -6841.37 | -7064.68 |
| Equilibrium concentration (nM) | 99.95 | 94.93 | 47.05 | 88.88 | 64.36 |
The second row shows the local secondary structure for the predicted RNA triplexes (grey: mRNA, green: miR-205-5p, red: other miRNAs). Seed distance: the distance between the seed sites of the miRNAs in the 3' UTR of E2F1. ∆G: the change in Gibbs free energy when the miRNA pairs and the E2F1 mRNA form the triplex (miRNA1/miRNA2/mRNAE2F1). ∆∆G: the free energy gained by triplex formation compared to the duplex (miRNA/mRNAE2F1) showing smaller ∆G. Potential energy: the calculated energy in the 3D structure of the triplexes. Equilibrium concentration: the equilibrium concentrations of RNA triplexes computed by a partition function algorithm (see Materials and Methods).
