Figure 2.
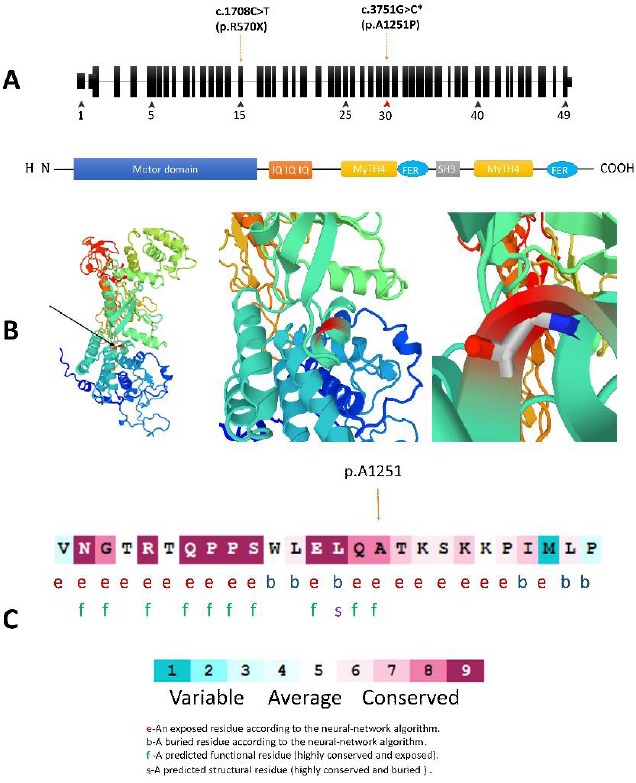
(A) Schematic structure of MYO7A and its encoded protein domains. The c.3735C>T located in the myosin tail homology 4 (MYTH4) domain that is coded by Exon 30. (B) A prediction of structural alternation resulted from MYO7A c. 3751G>C mutation designed by SWISS-MODEL and PMP online tools. This substitution is not conserved because the substituted amino acid, Proline, has poor helix-forming propensity and it can stir the secondary structure in this protein. (C) Multiple alignments of the MYO7A c.3751G homologous sequences of eight different vertebrates based on UCSC Multiz alignments tool. The amino acid substituted by the missense mutation p.A1251P (the red types) is highly conserved among the different vertebrate species. (D) The amino acid sequence MYO7A (p.Ala1251) colored based on conservation scores by ConSurf database. ConSurf demonstrates evolutionary conservation profiles for proteins of known structure in the PDB according to the phylogenetic relations between homologous sequences as well as amino acid’s structural and functional importance
