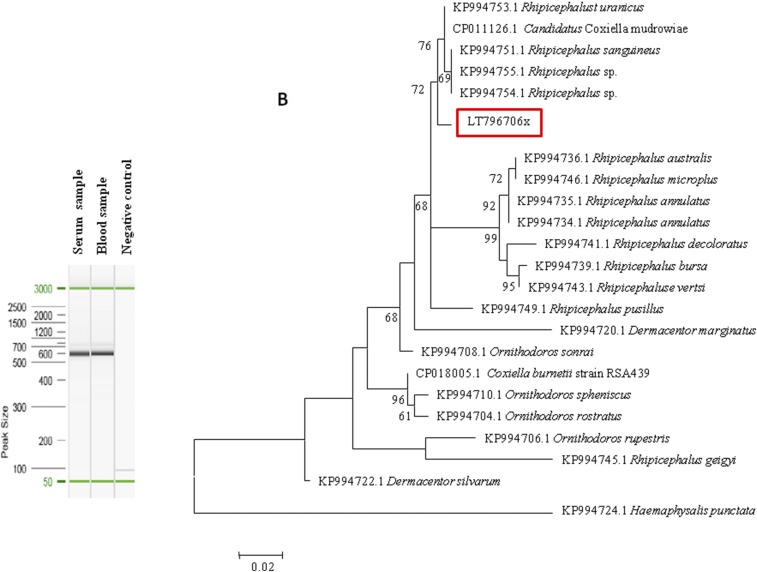
Figure 2.
(A) 23S ribosomal RNA gene nested PCR assay electrophoresis in agarose gel; (B) maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree based on 23S ribosomal RNA gene sequences including Coxiella-like strains of ticks. The sequences were aligned using CLUSTALW. Phylogenetic inferences were performed with the maximum likelihood and neighbor-joining (NJ, see Supplemental Figure 1) methods under the Kimura 2-parameter model and complete deletion. Both trees were run using MEGA software.16 The robustness of the nodes in both ML and NJ trees was estimated through bootstrap analyses of 500 and 1,000 replicates, respectively. GenBank accession numbers are indicated in the beginning, followed by the tick host. This figure appears in color at www.ajtmh.org.