Fig. 1.
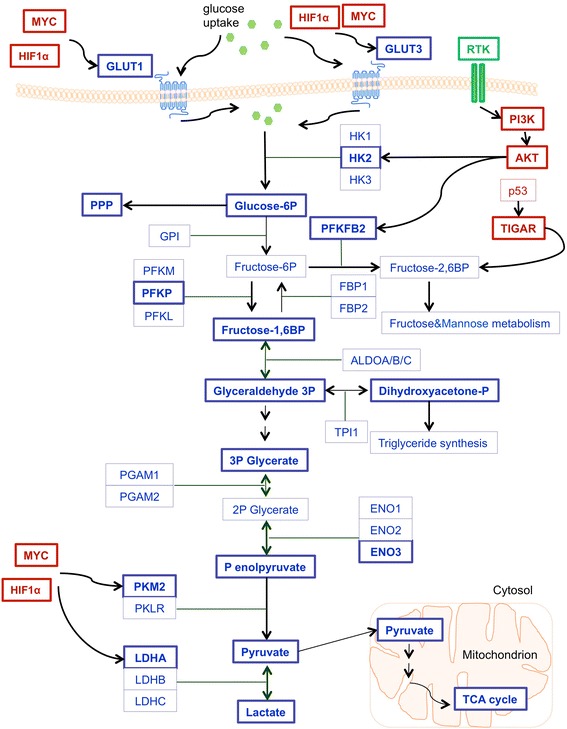
TKI-induced regulation of glycolytic pathway. Highlighted in bold are proteins and metabolites (blue) together with glycolytic regulators (red) that were shown to be affected by the inhibition of TKs. Abbreviations: GLUT1/3—glucose transporter 1/3; HK1/2/3—hexokinase 1/2/3; TIGAR—TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; P—phosphate; BP—bisphosphate; PPP—pentose phosphate pathway; GPI—glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; PFKFB2— 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 2; PFK—6- phosphofructokinase(three isoforms – muscle (PFKM), liver (PFKL) and platelet (PFKP)); FBP1/2—fructose-bisphosphatase 1/2; ALDOA/B/C—aldolase A/B/C; TPI1—triosephosphate isomerase; PGAM1/2—phosphoglycerate mutase 1/2; ENO1/2/3—enolase 1/2/3; PKM2—pyruvate kinase isozyme M2; PKLR—Pyruvate kinase isozymes L/R; LDHA/B/C—lactate dehydrogenase A/B/C; TCA cycle—tricarboxylic acid cycle
