Fig. 1.
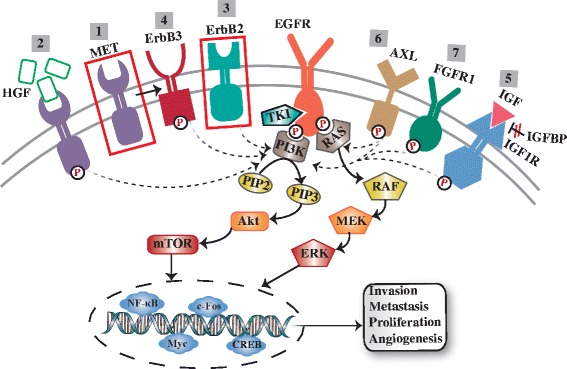
Secondary RTKs-induced EGFR-TKIs resistance. EGFR could trigger downstream PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling axes which in turn stimulate the transcription factors to drive the associated genes expression which are related with proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis. TKIs inhibit EGFR-drived signal transduction by interacting with the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR. Other RTKs are involved in the development of TKIs resistance via a EGFR-indepenfent way: 1. Amplification of MET activates PI3K through transactivating ErbB3; 2. HGF overexpression; 3. ErbB2 amplification; 4. ErbB3 activation; 5. IGF1R activation by IGF binding or IGFBP reduction; 6. AXL activation; 7. FGFR1 activation
